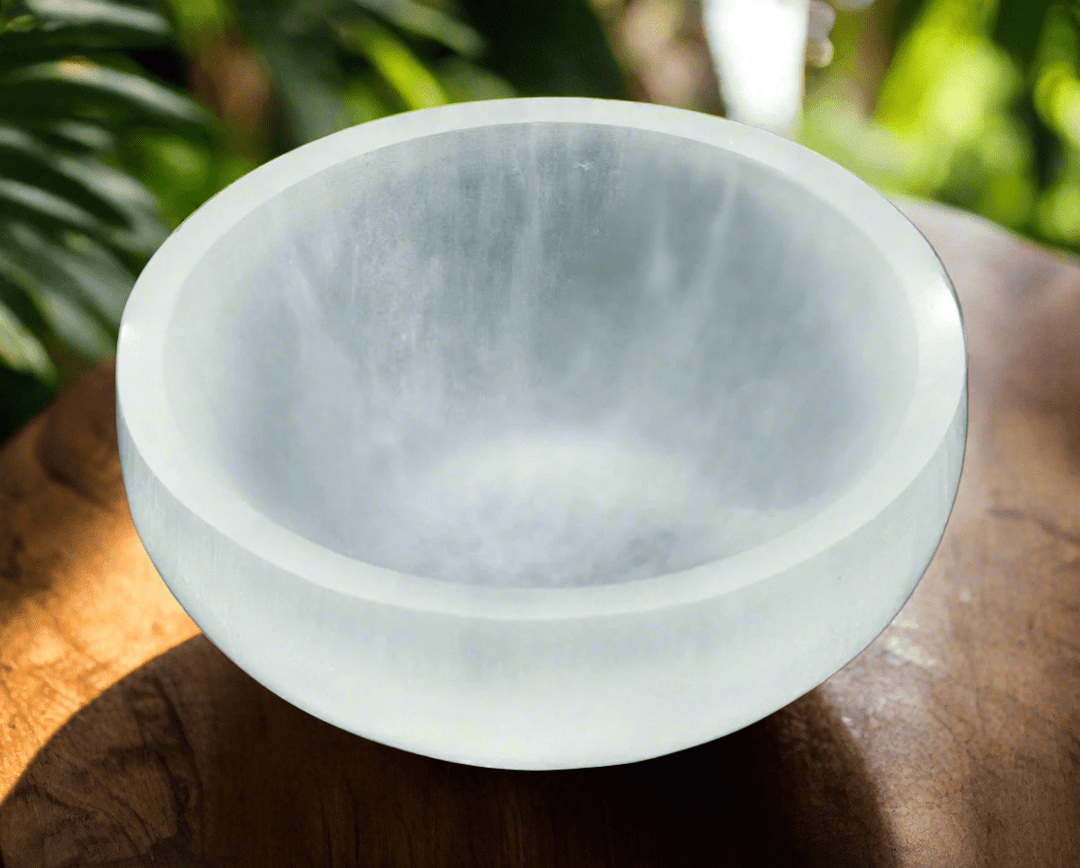
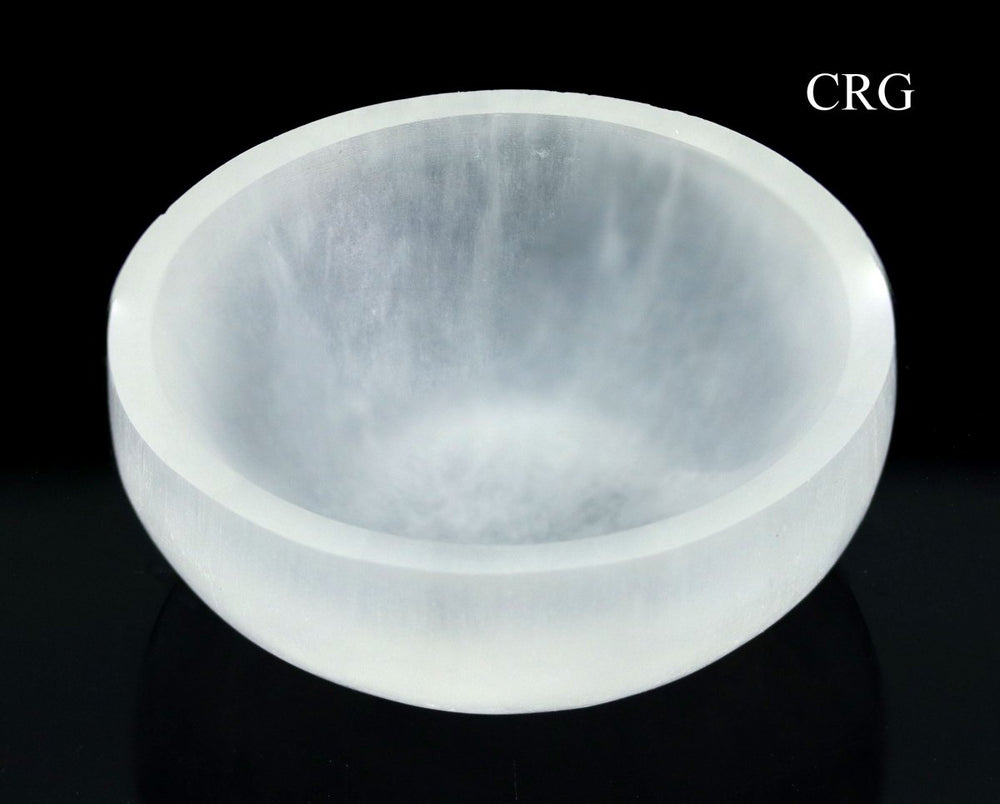
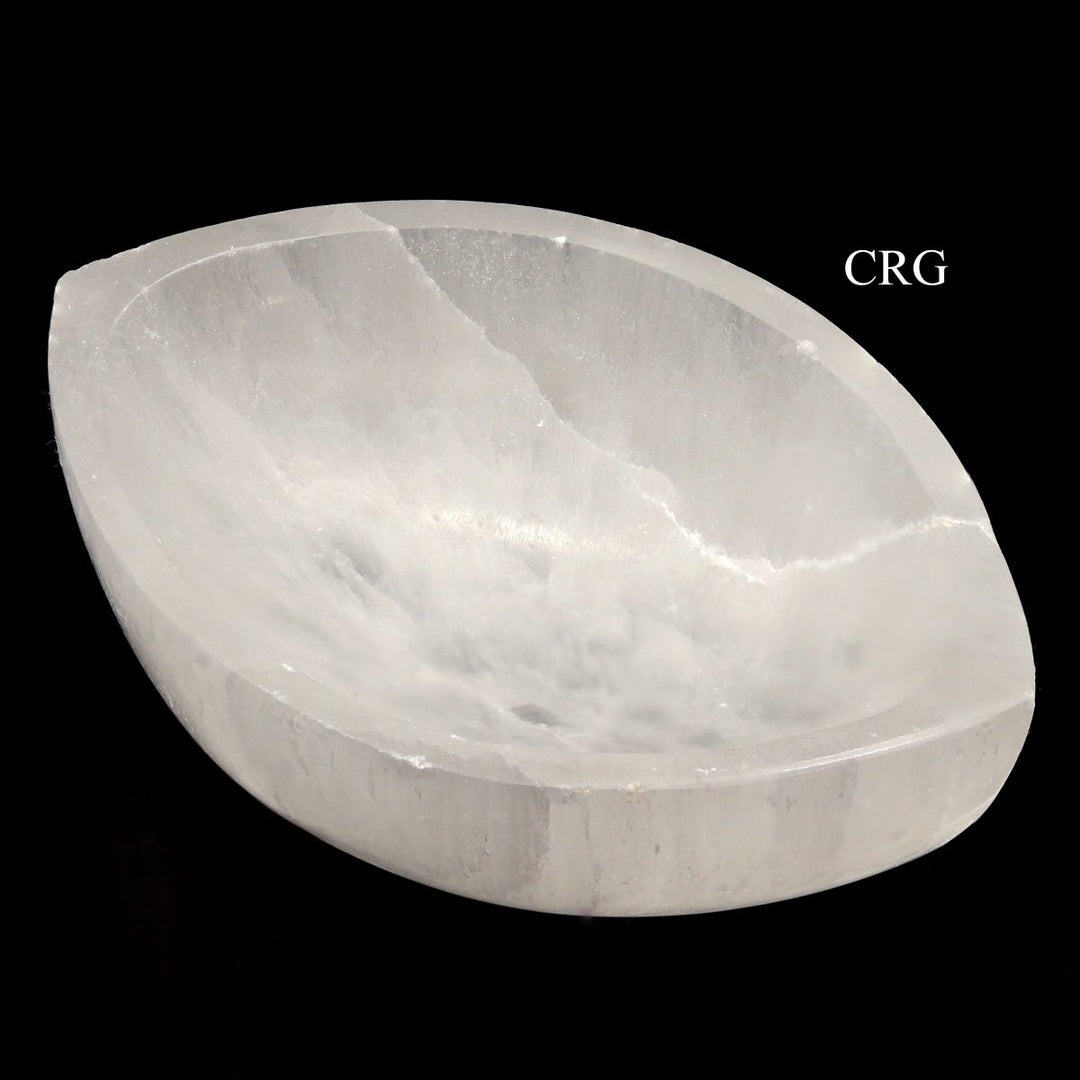
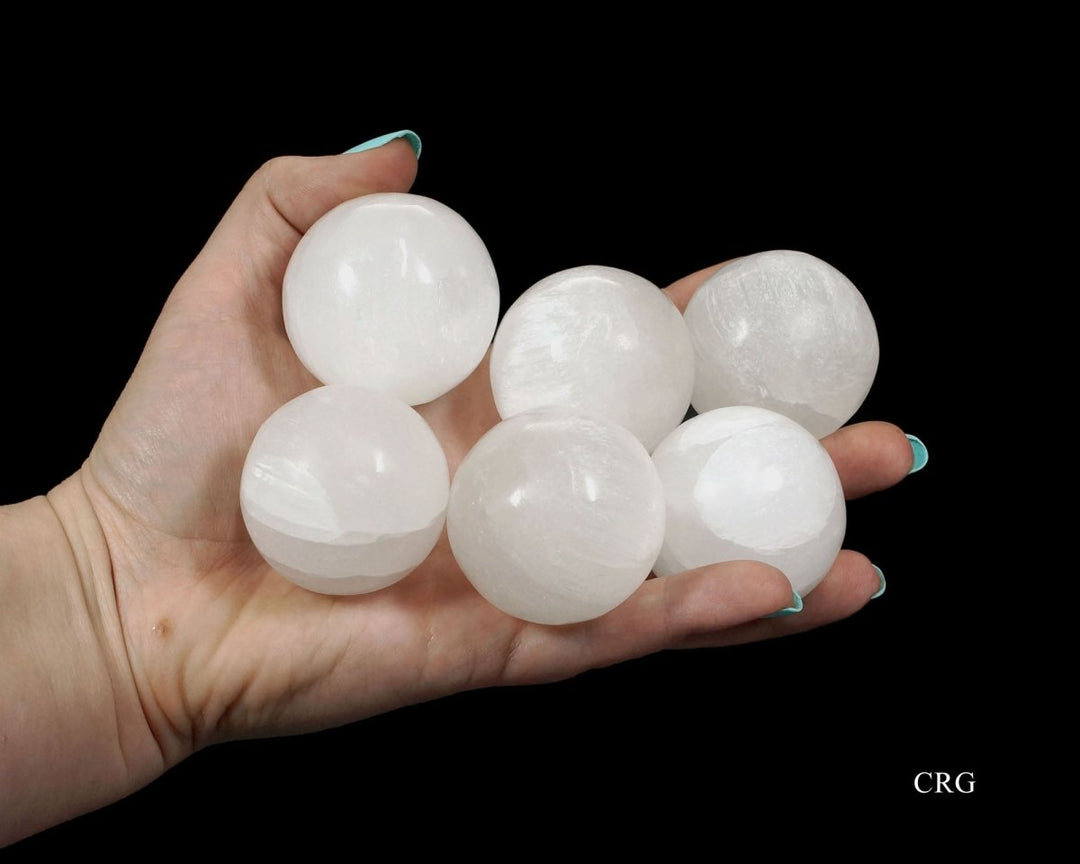
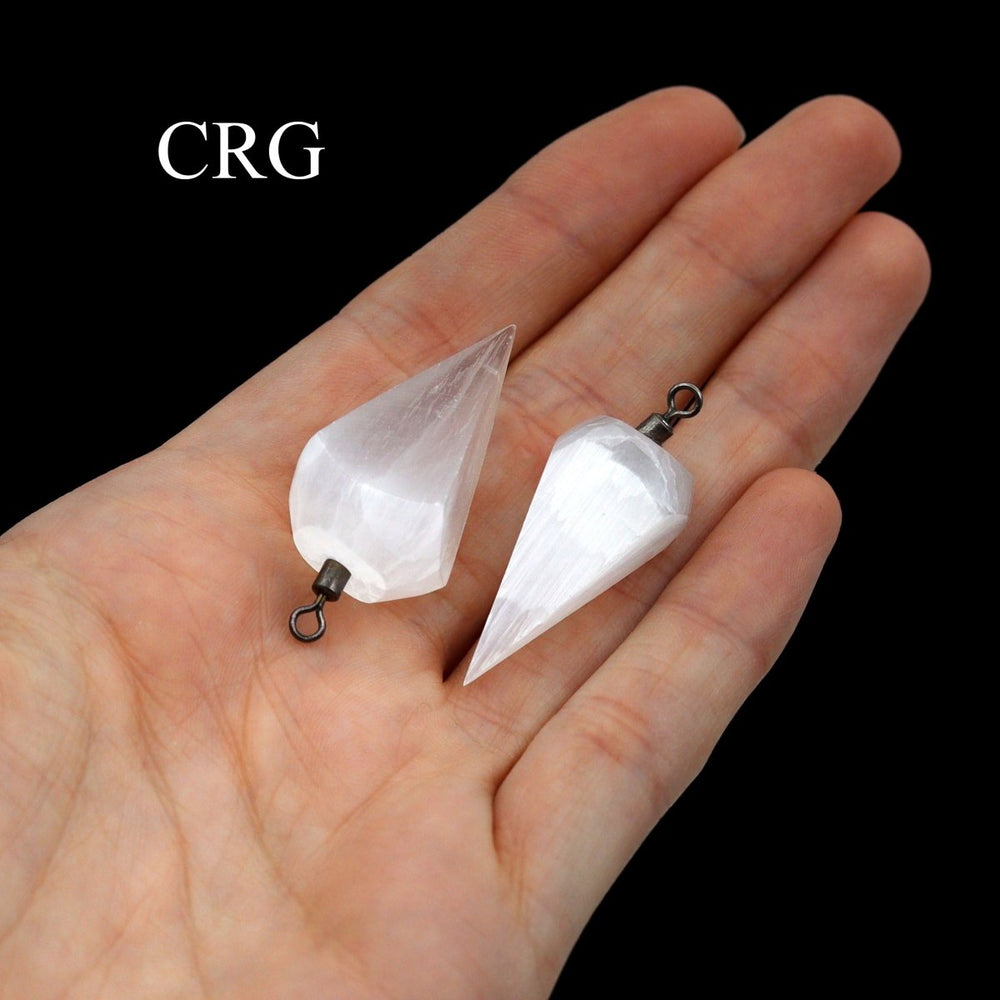
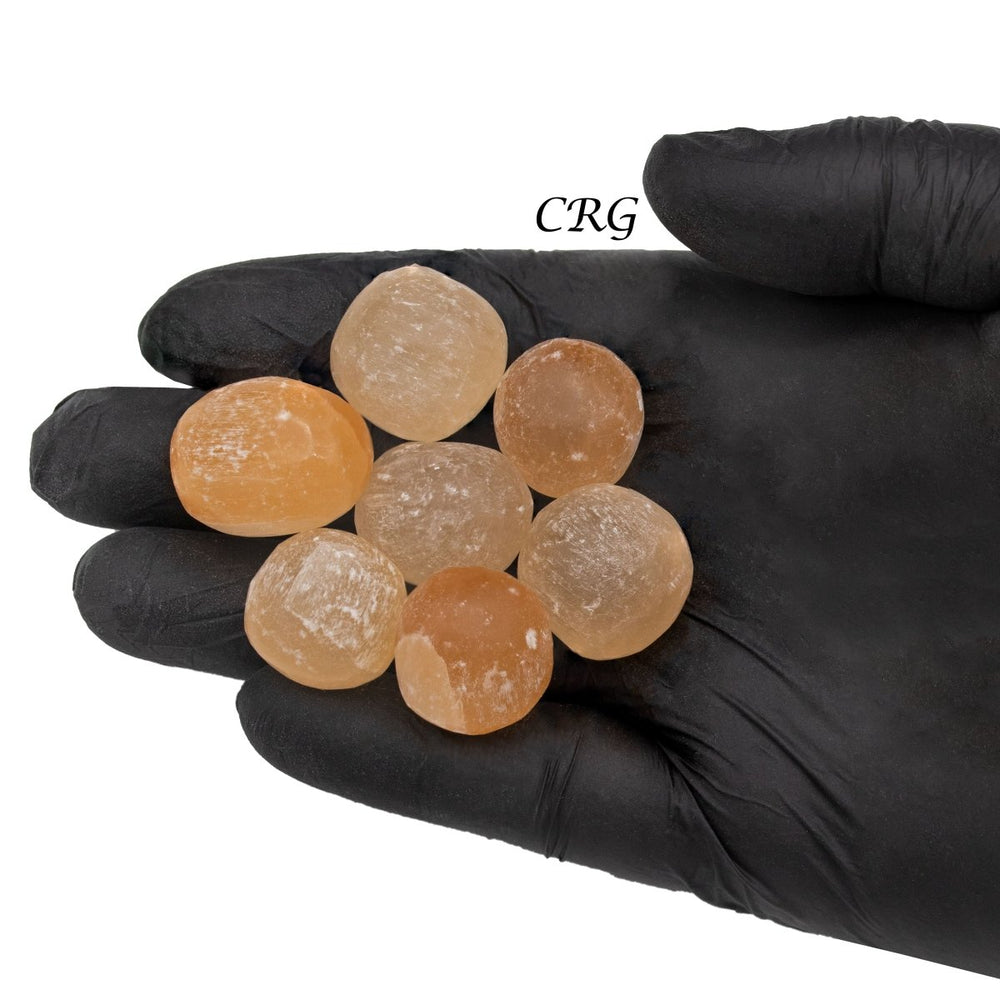
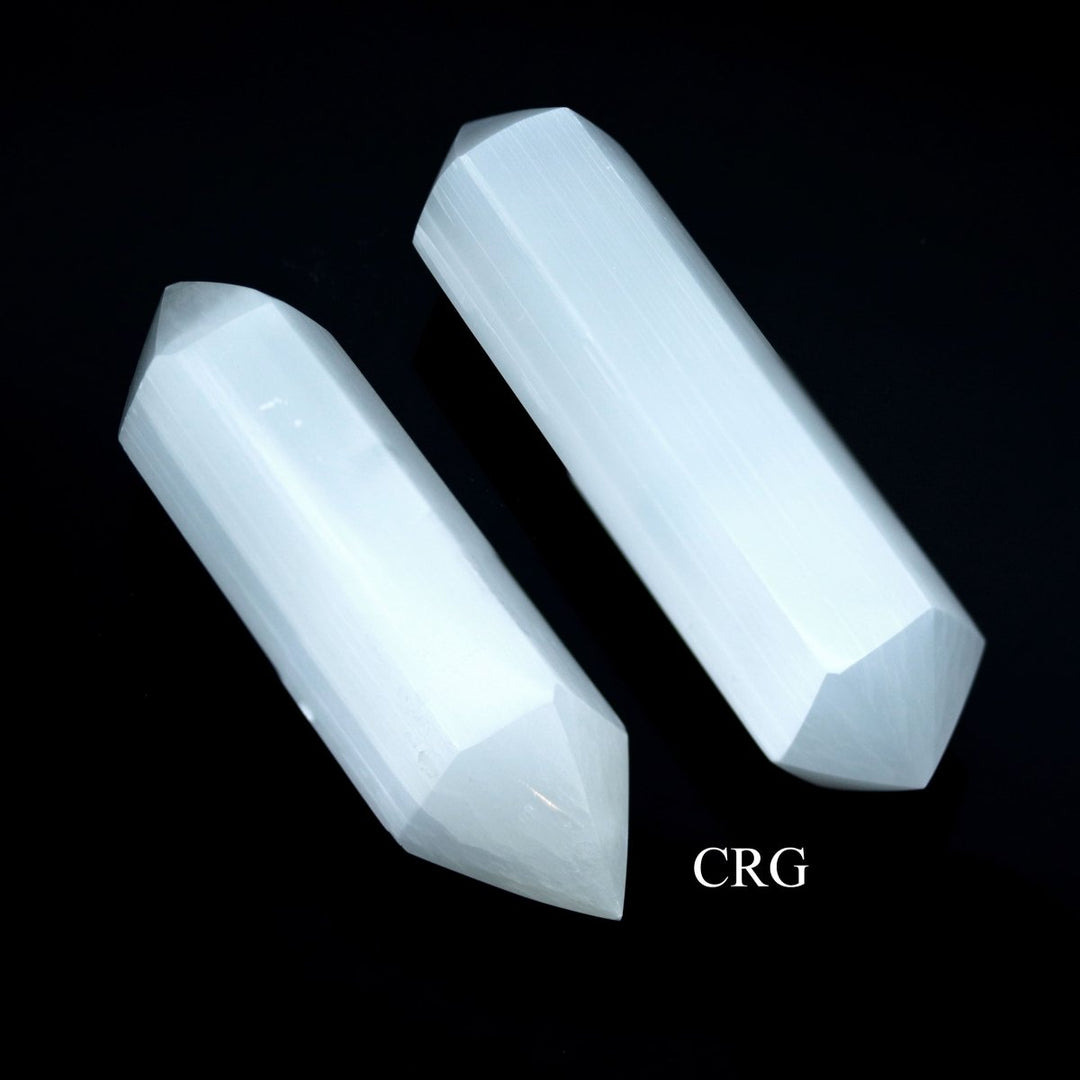
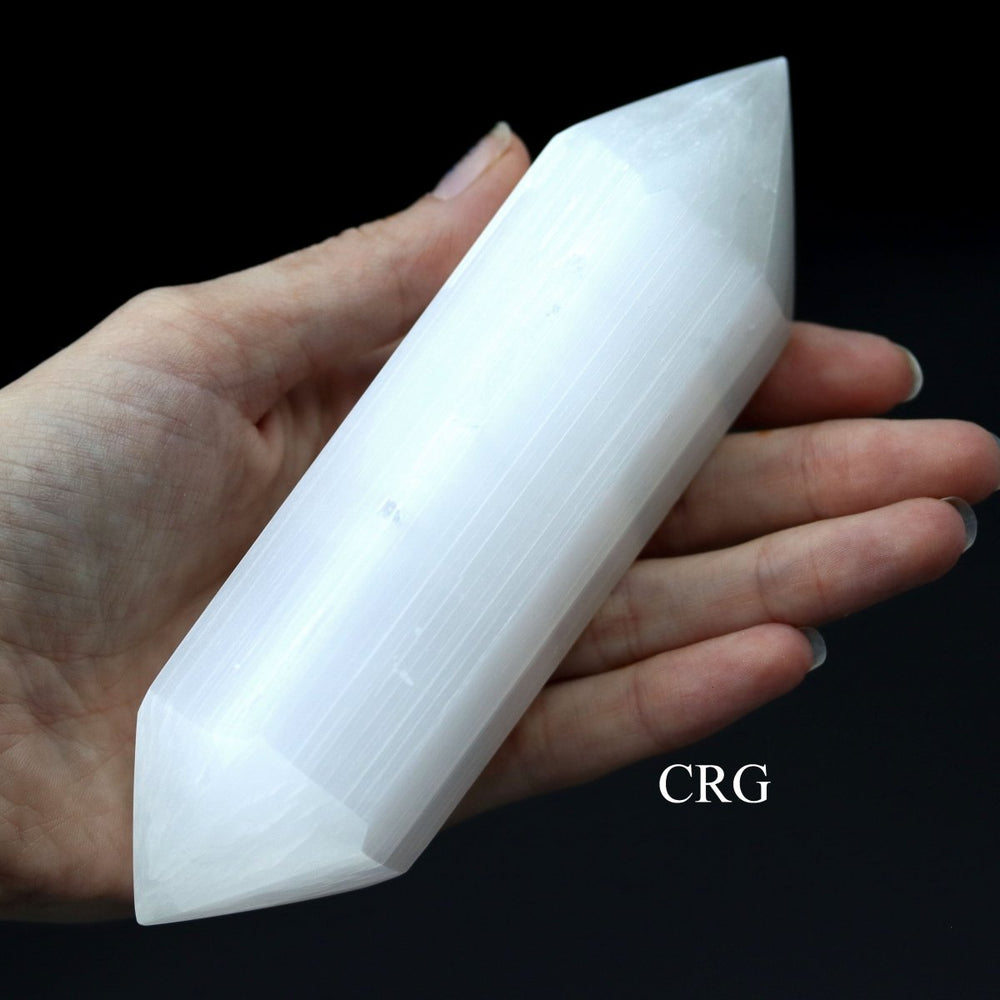
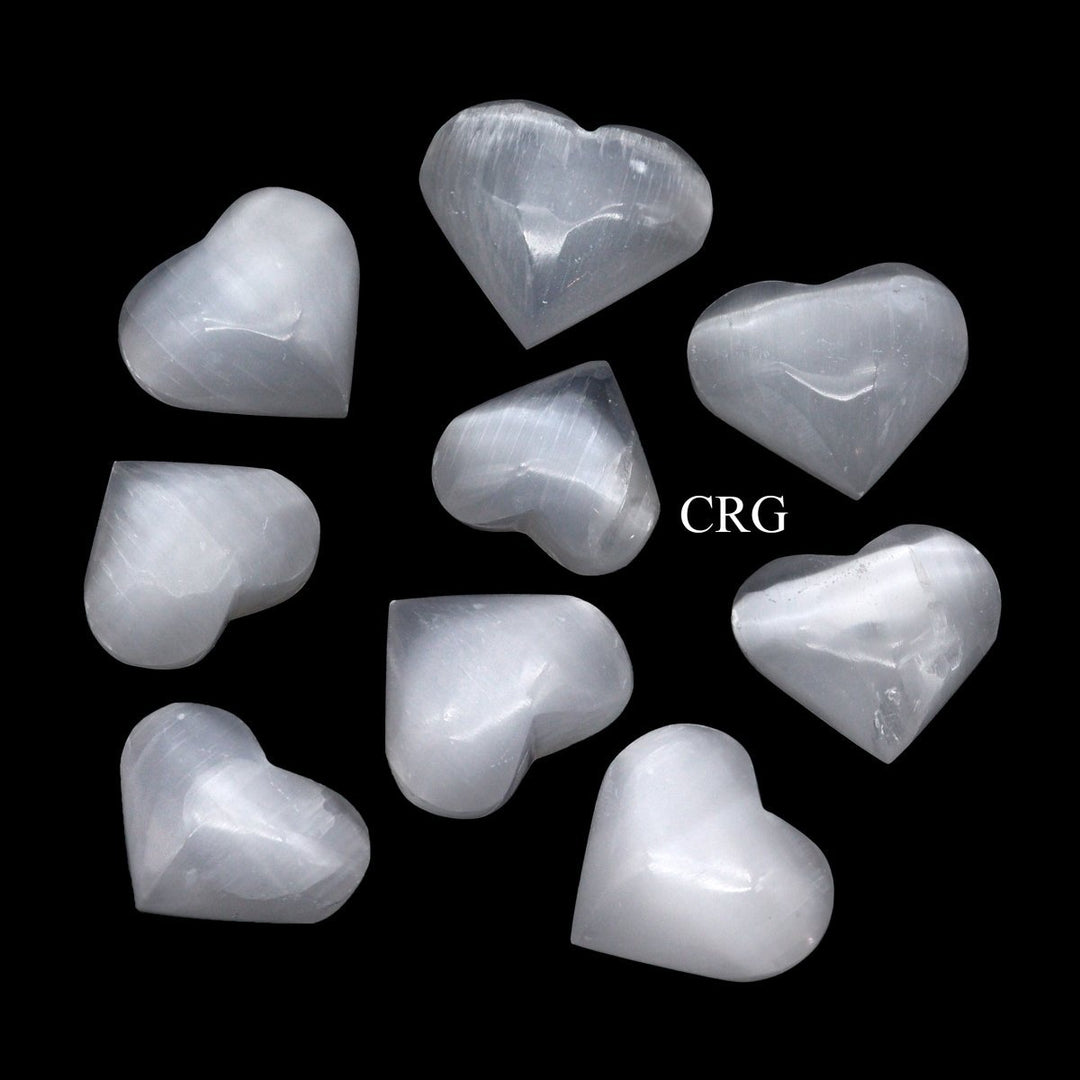
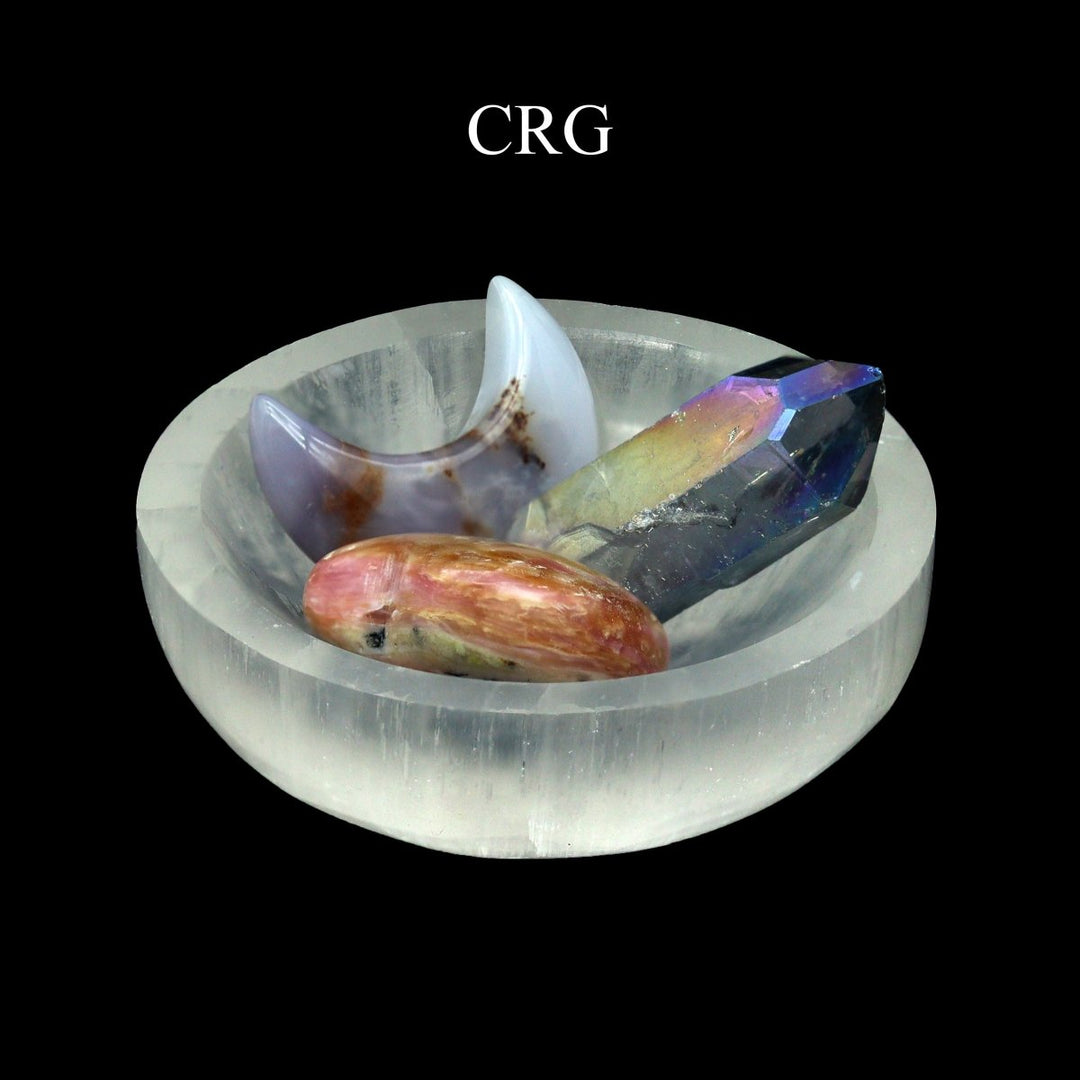
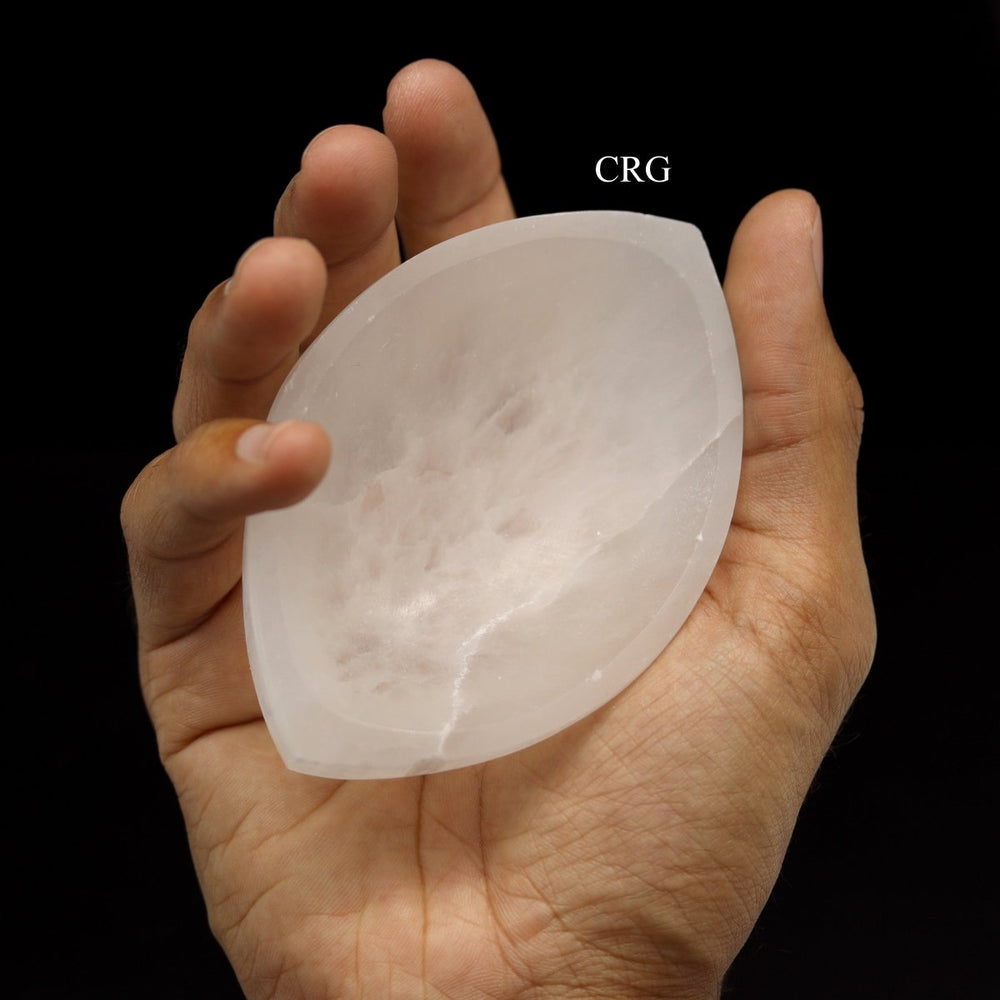
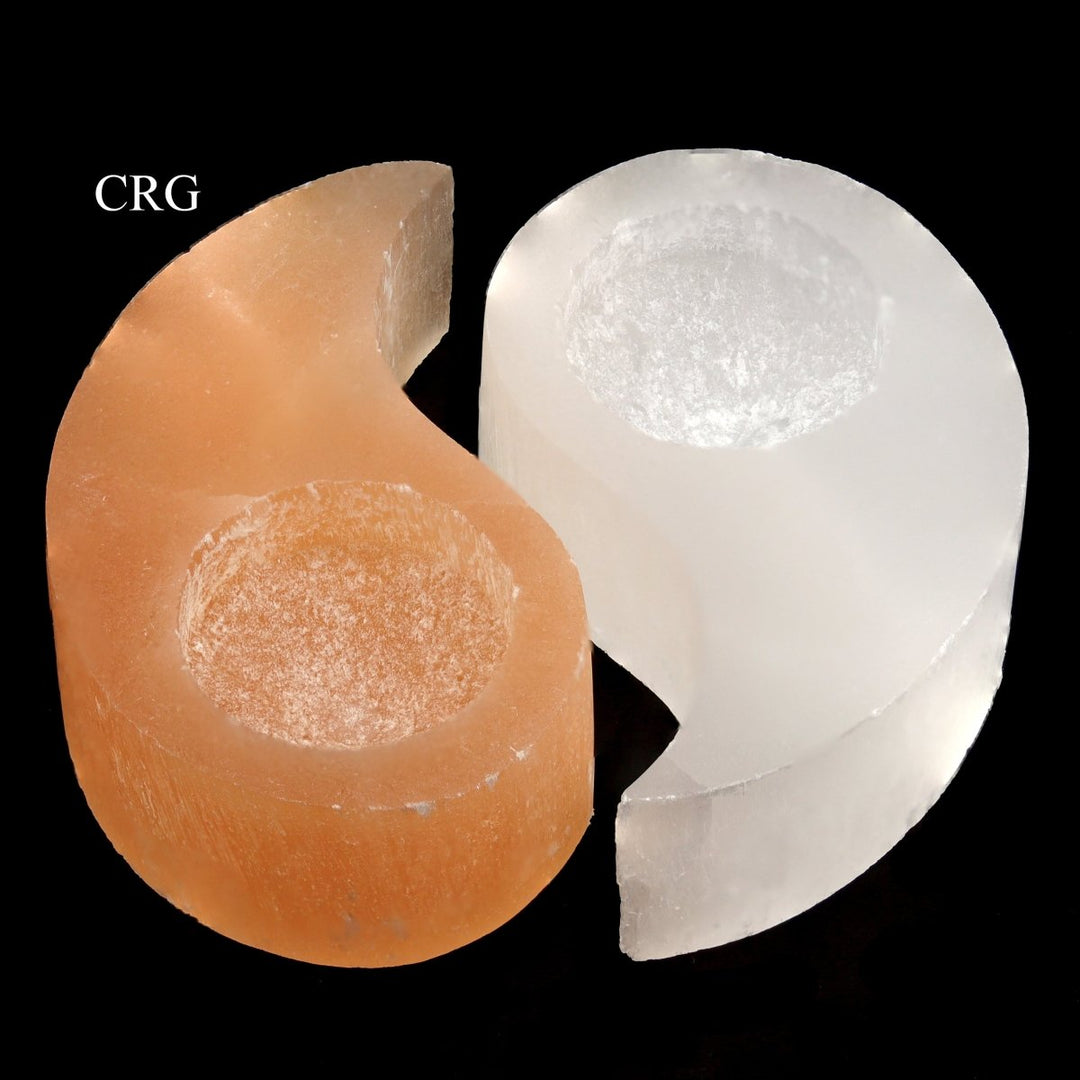
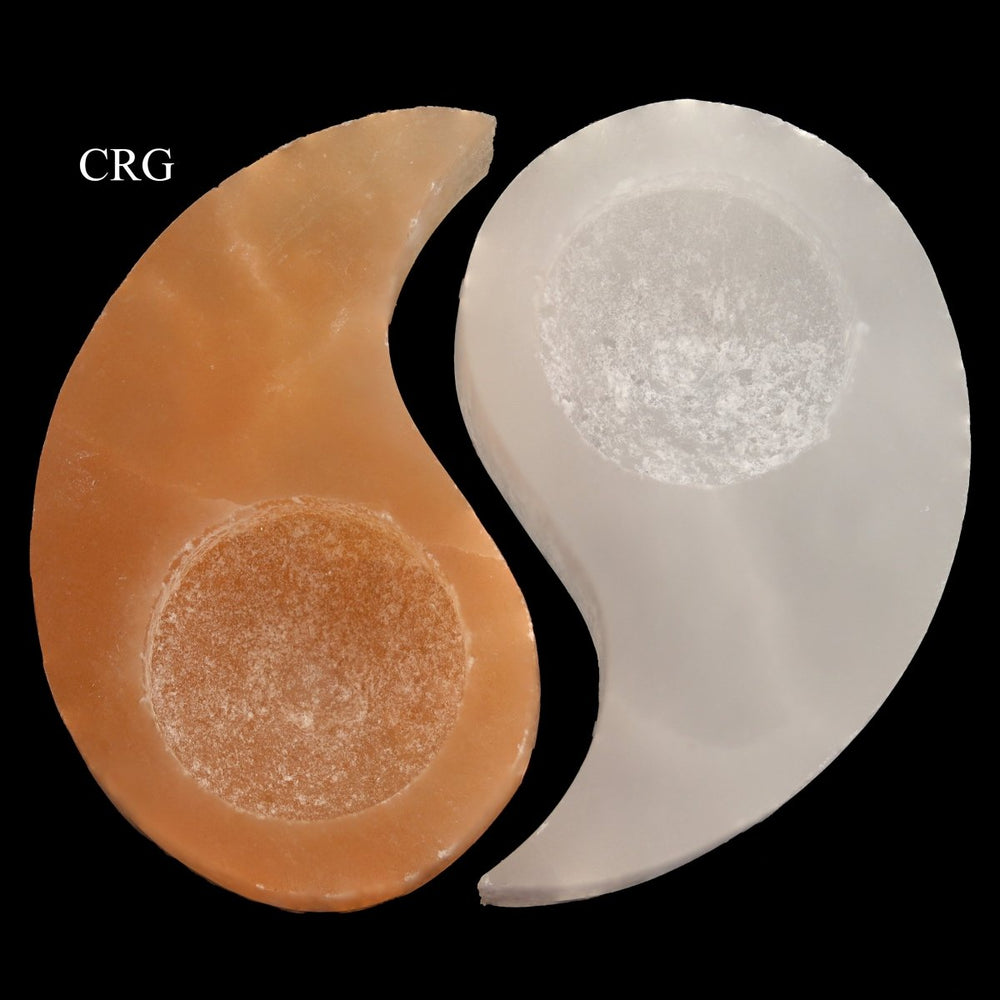
Selenite
Selenite is a crystalline form of gypsum, which is a hydrated calcium sulfate mineral with the chemical formula CaSO₄·2H₂O. Selenite forms in evaporative environments such as salt flats, hot springs, and areas with a high concentration of sulfate solutions where water evaporates and leaves behind sulfate minerals. It can also form as secondary crystals in sedimentary rocks, filling cracks where these solutions have flowed through. Selenite is translucent to transparent, which allows light to pass through it easily, creating a luminous effect. It's known for its fibrous, striated crystals, and it has a Mohs hardness of only 2, making it quite soft and flexible. One of the most remarkable properties of selenite is its ability to form in long, columnar crystals that can be peeled into thin, transparent sheets.