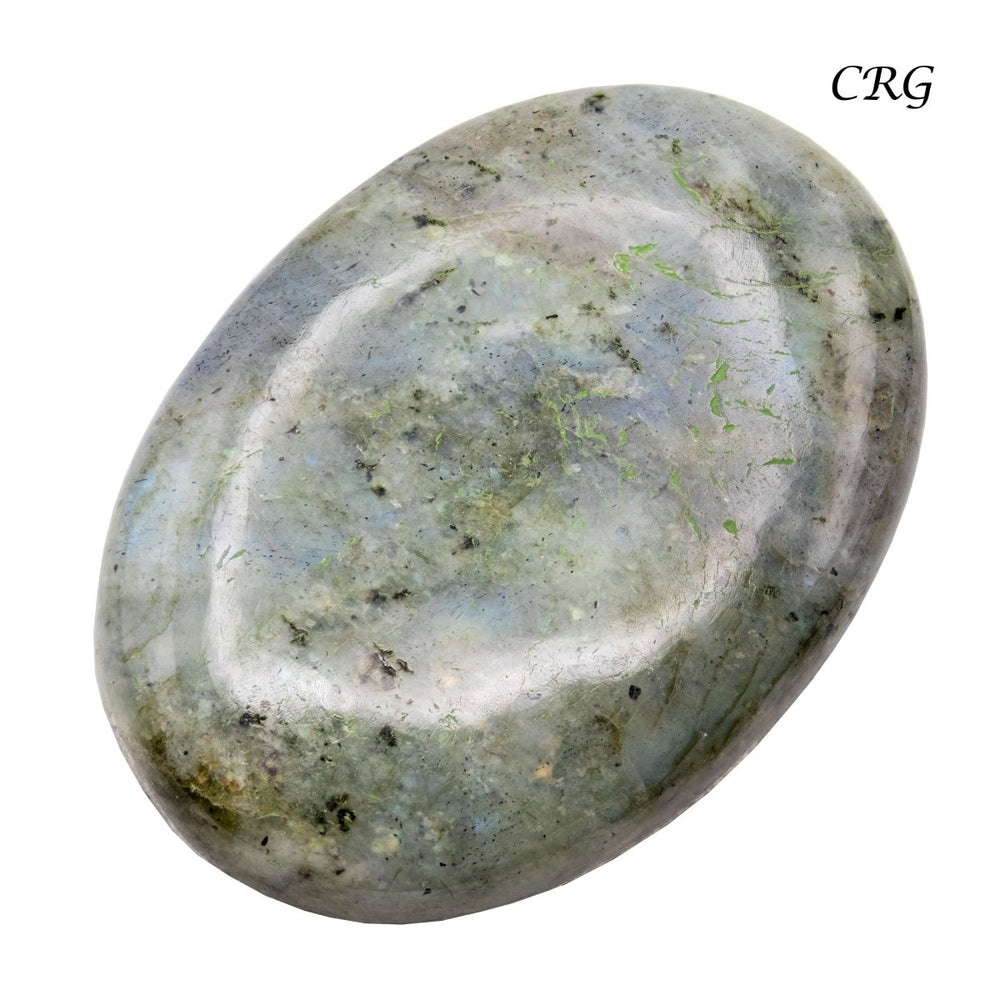
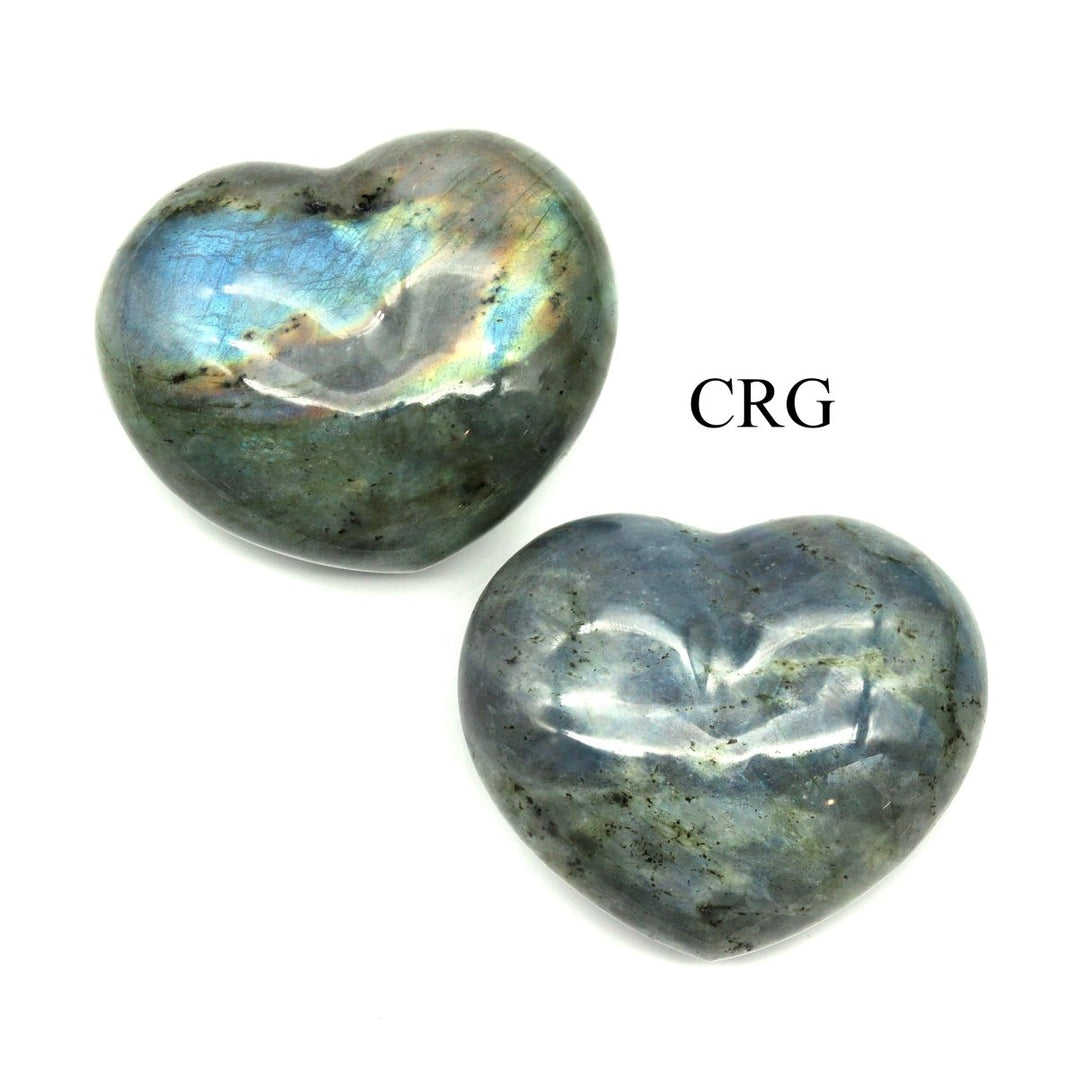
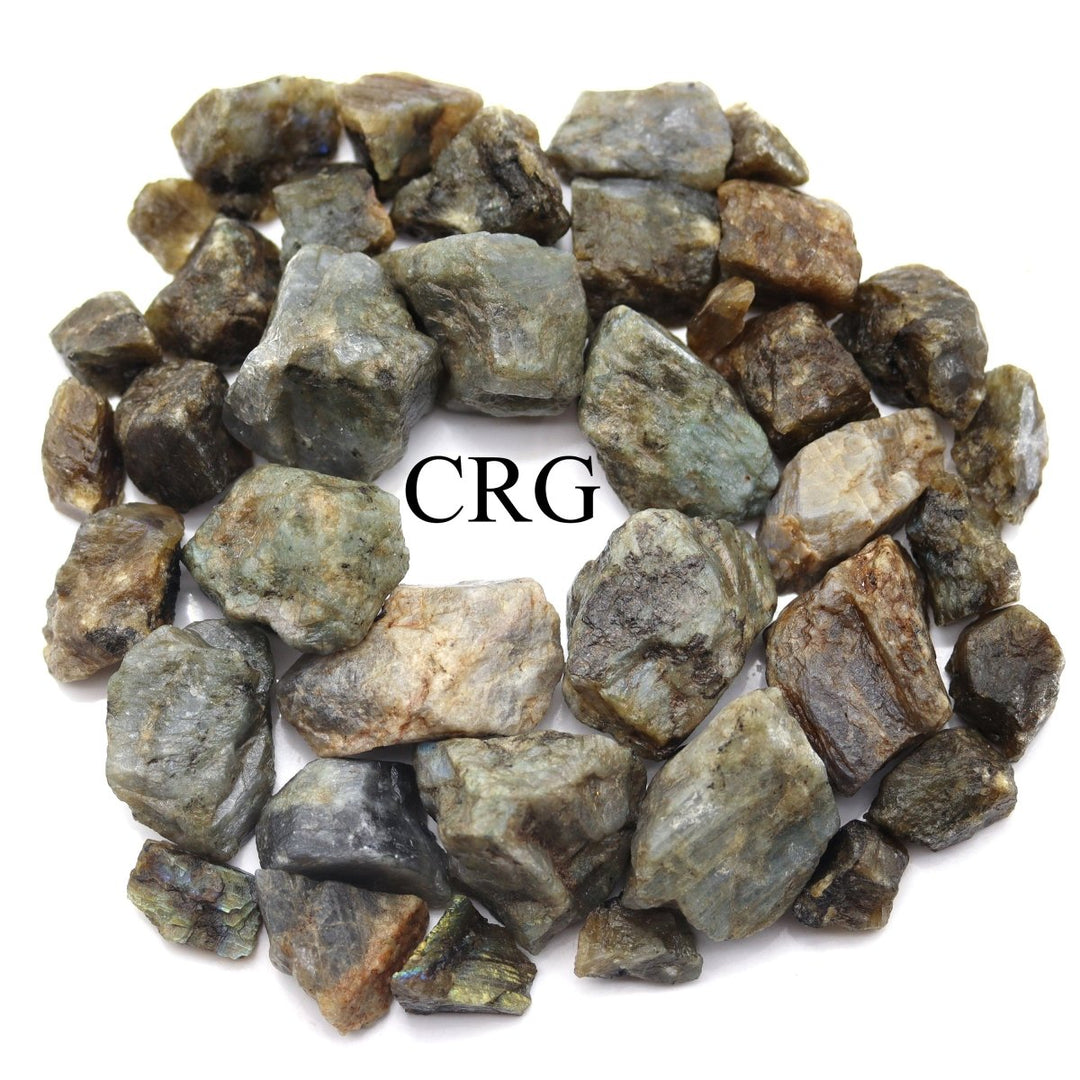
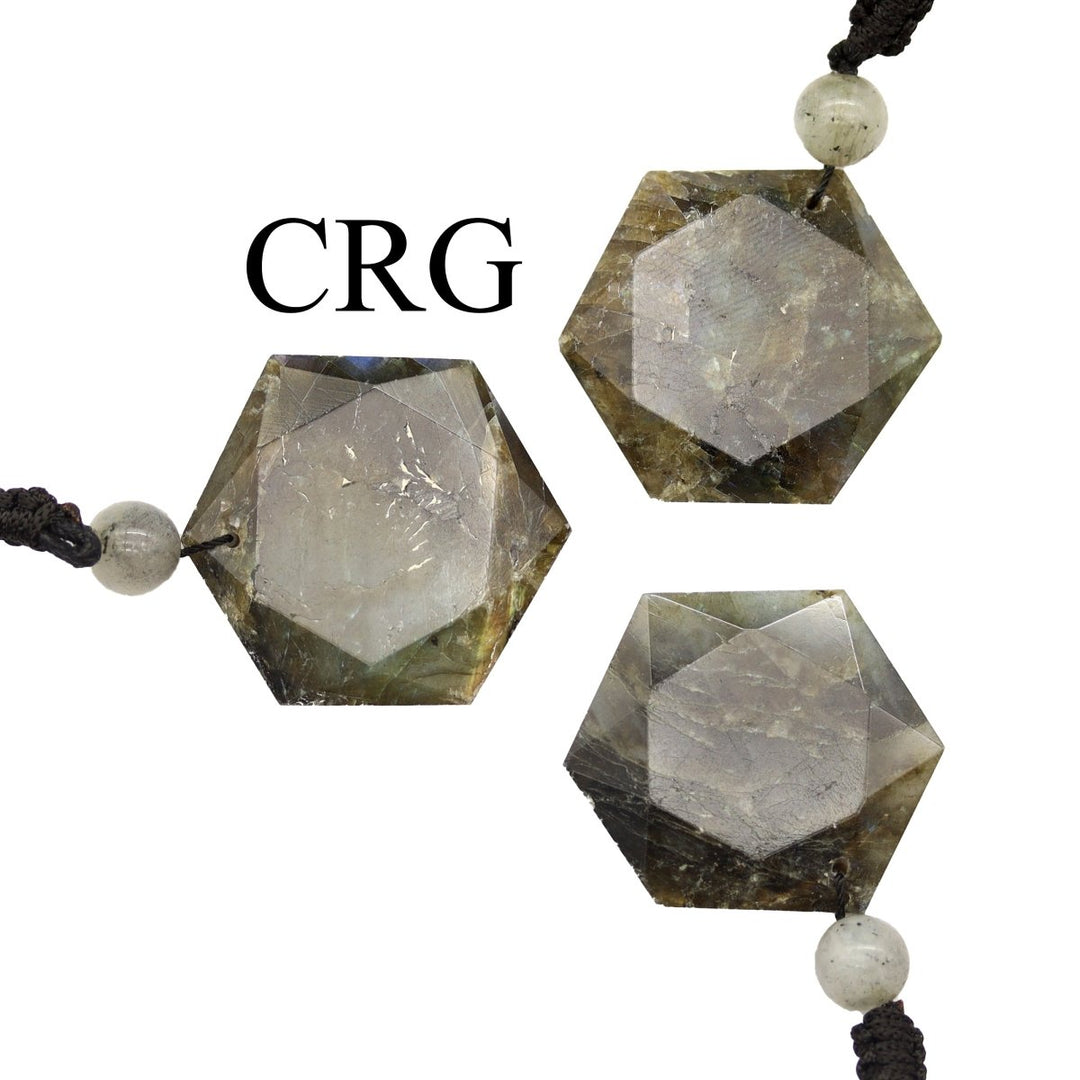
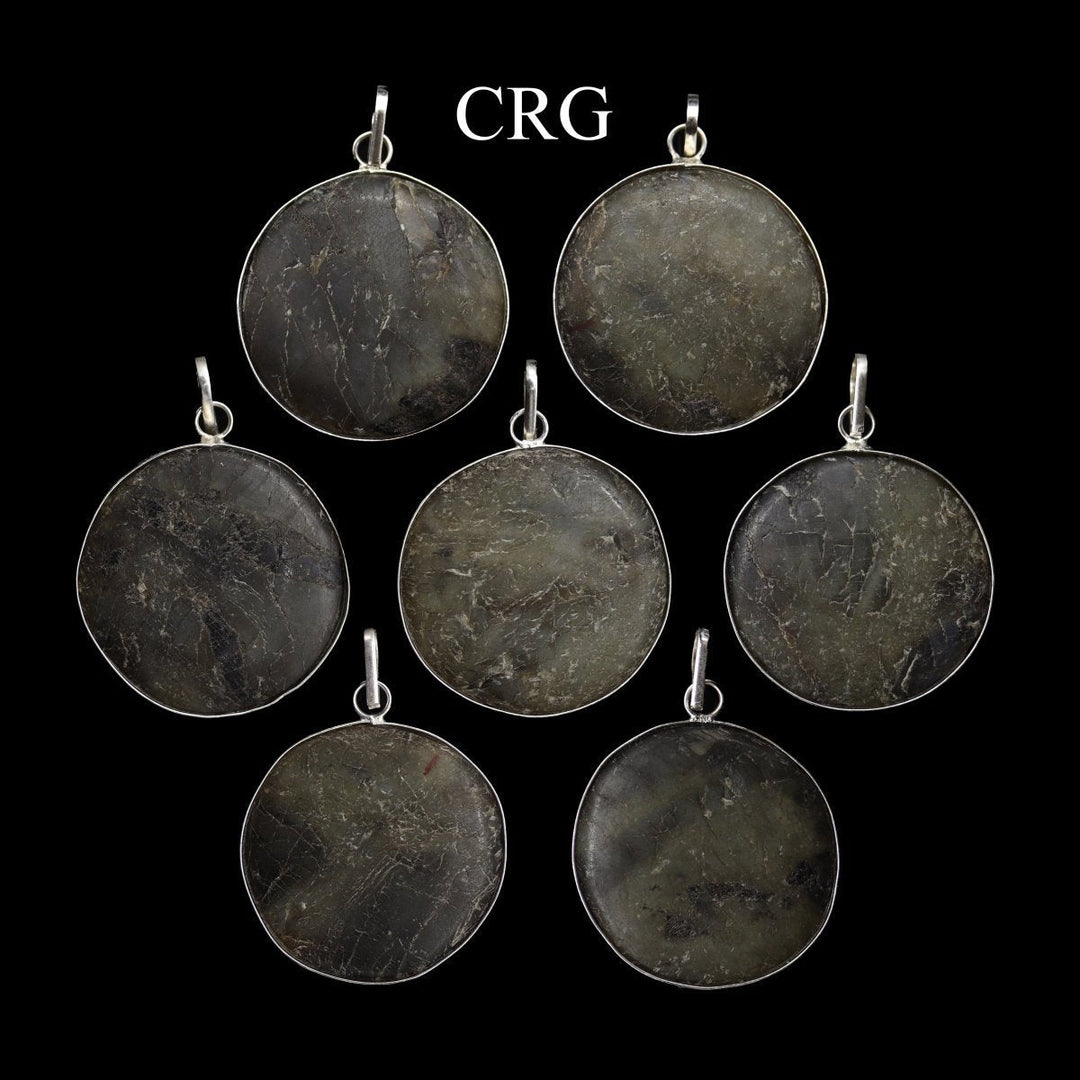
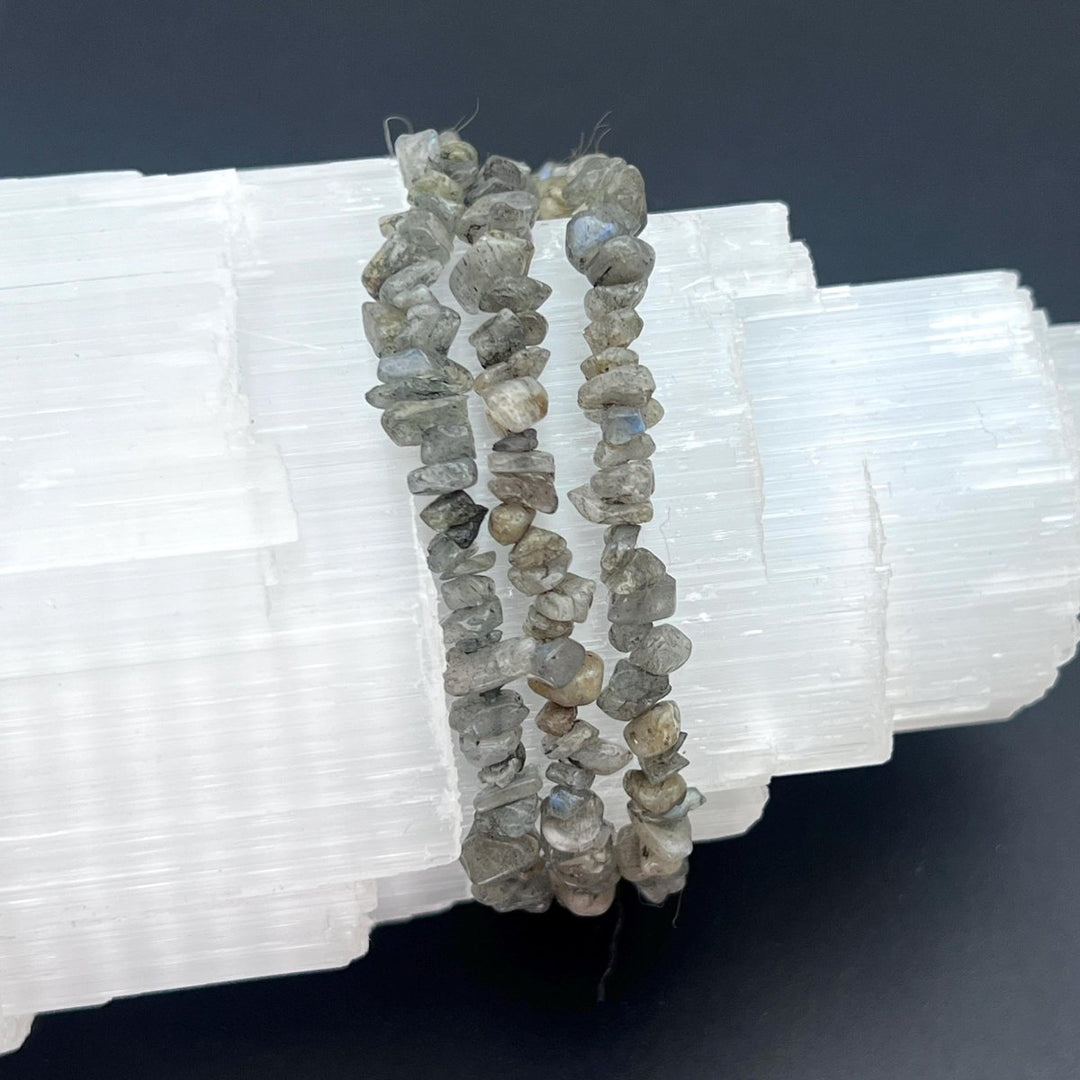
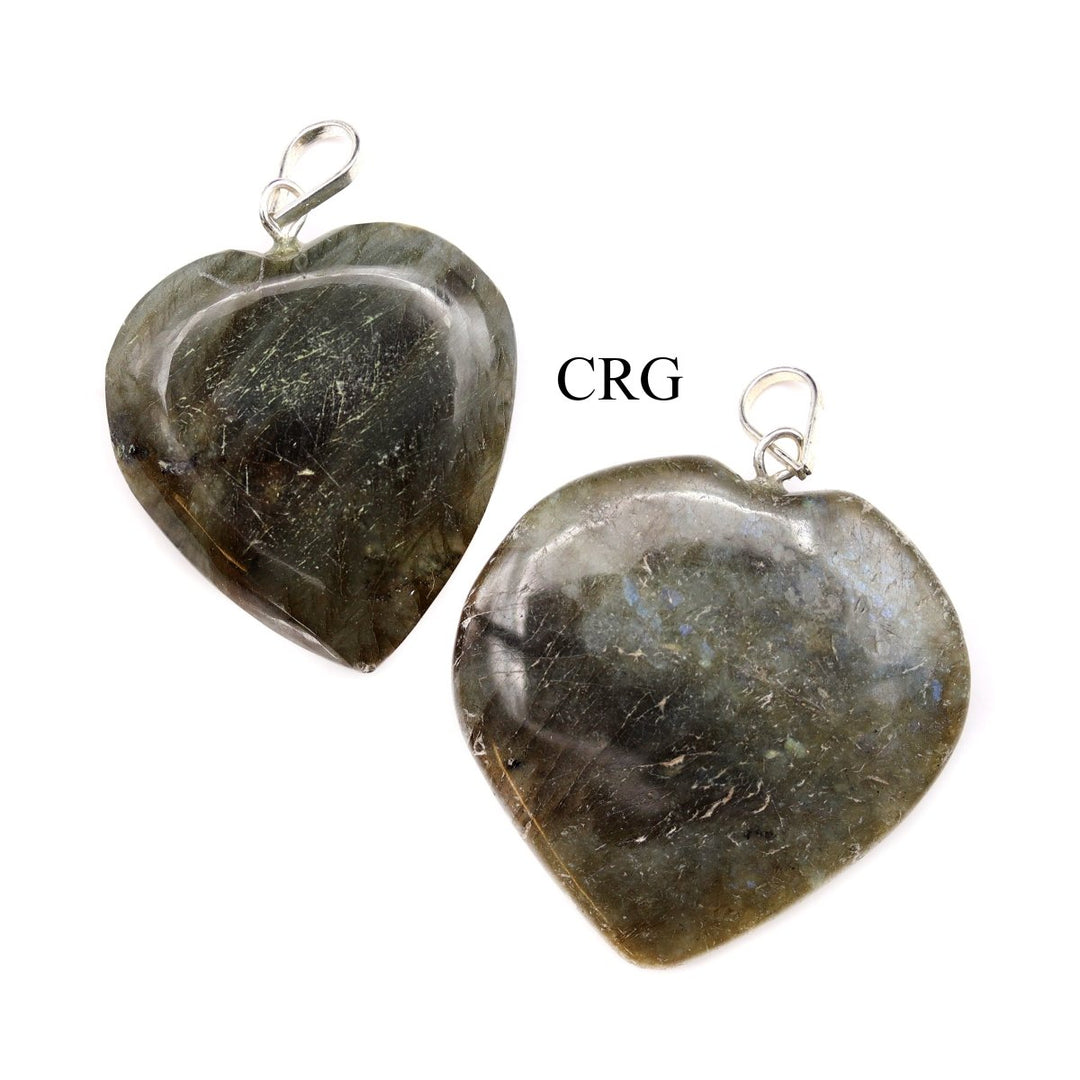
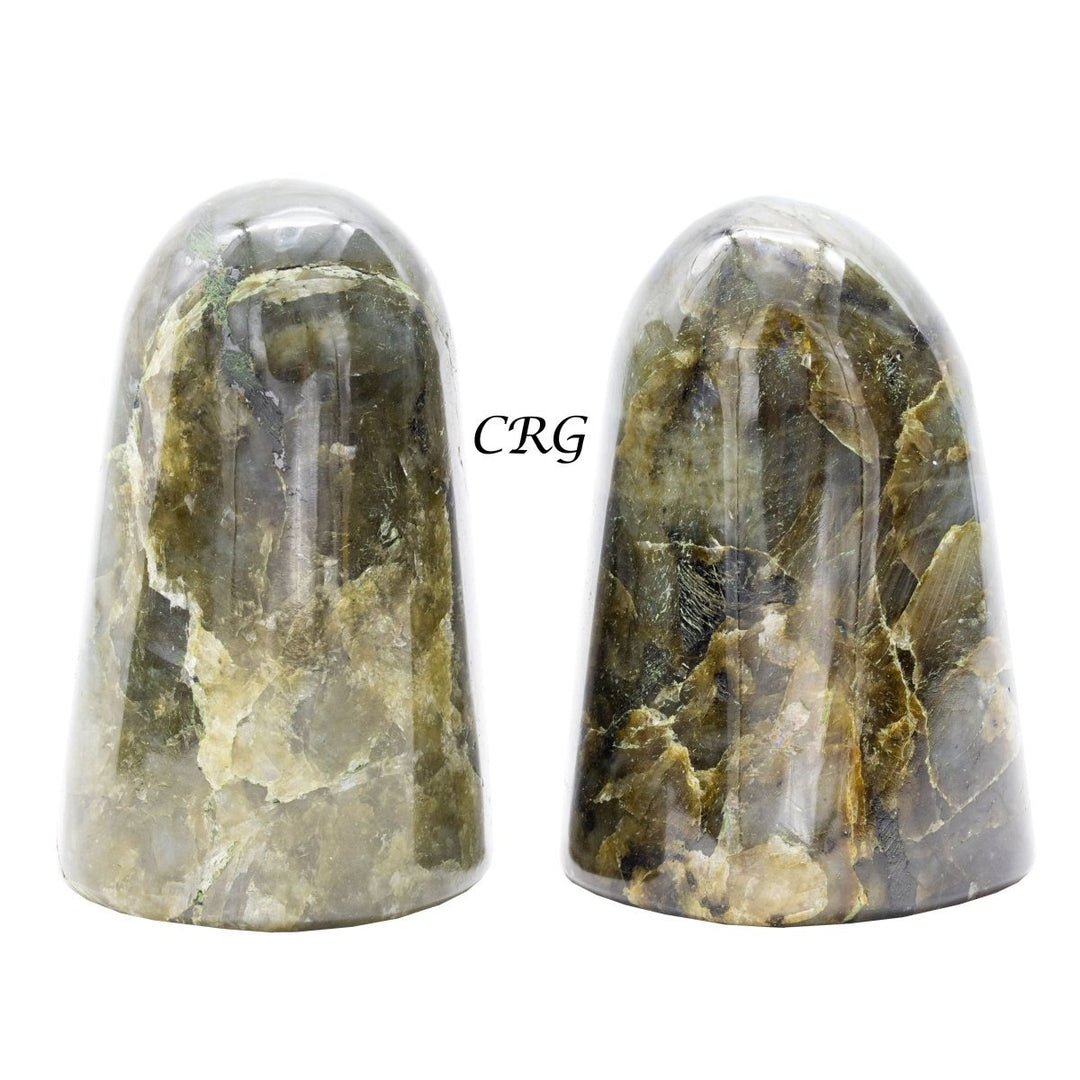
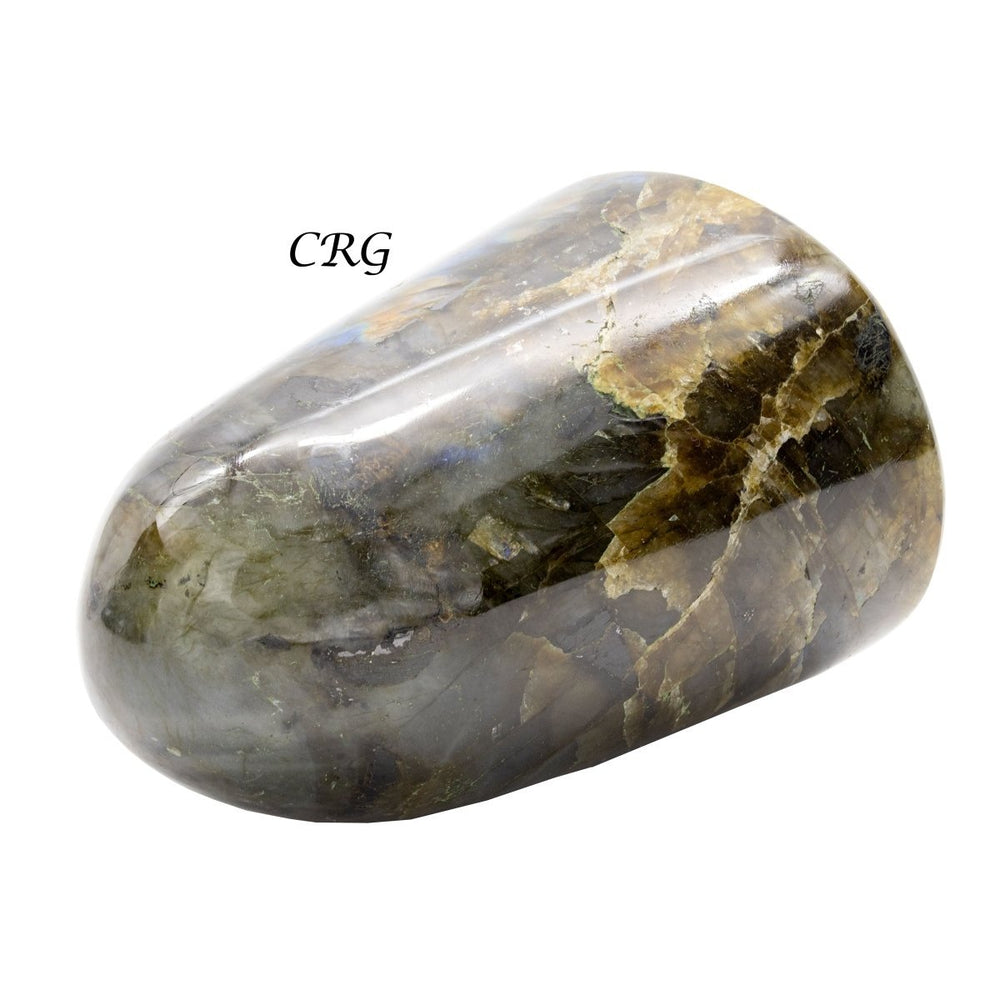
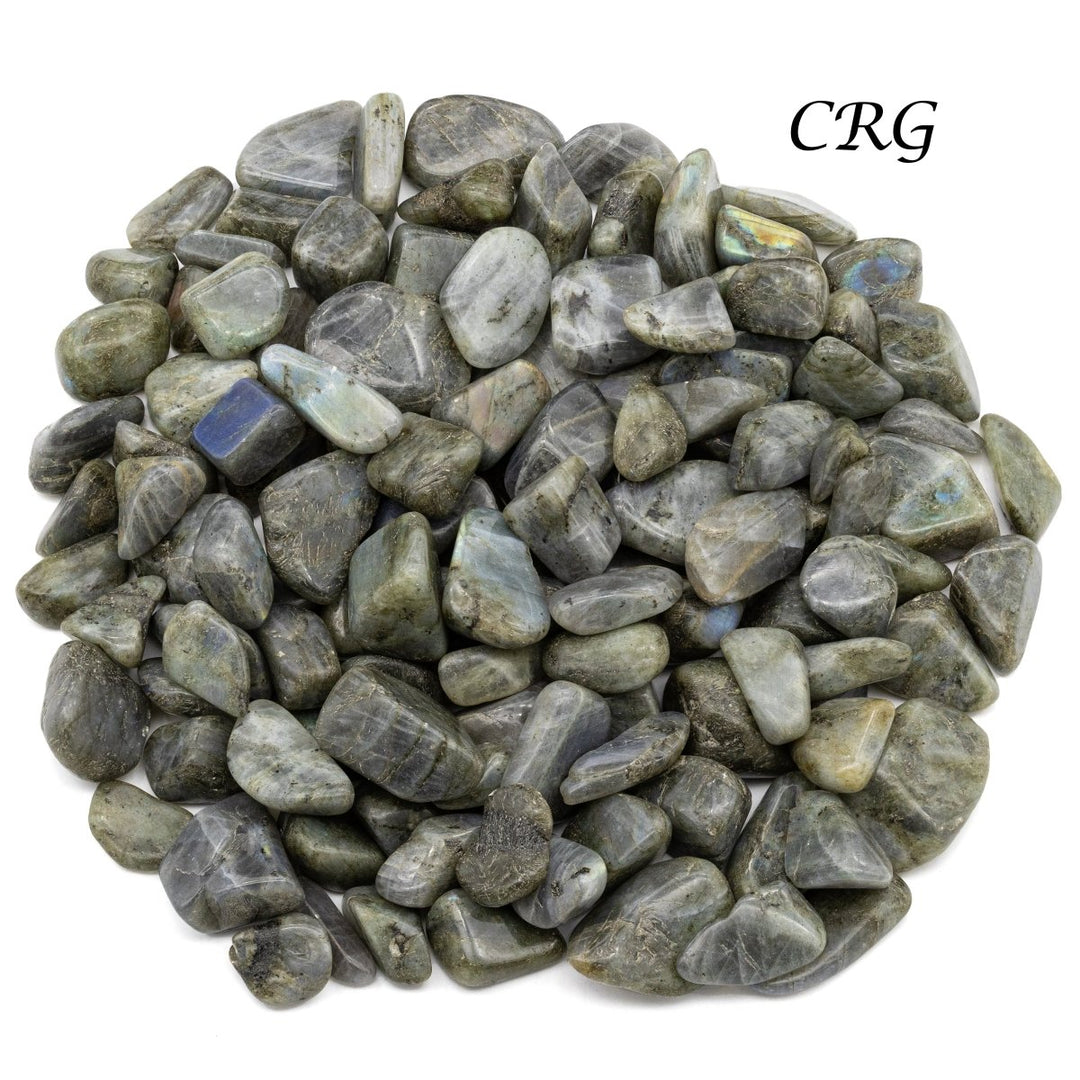
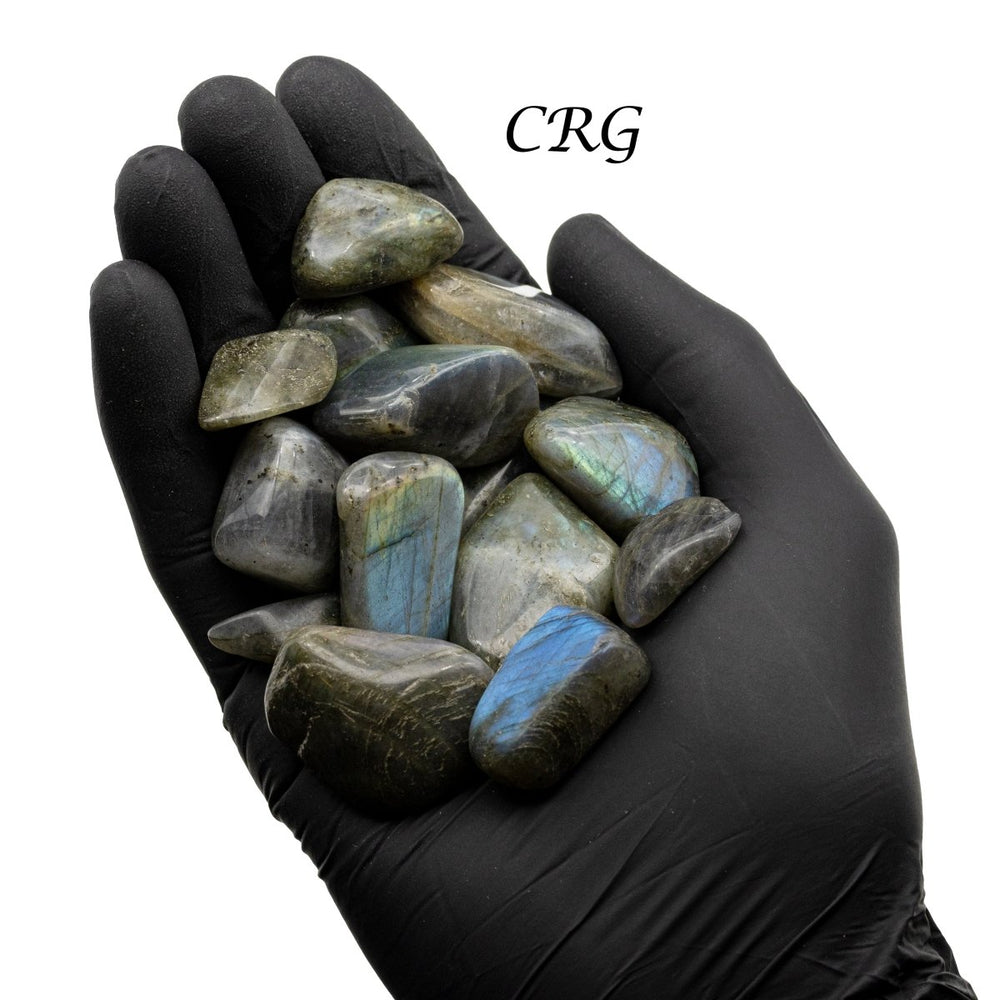
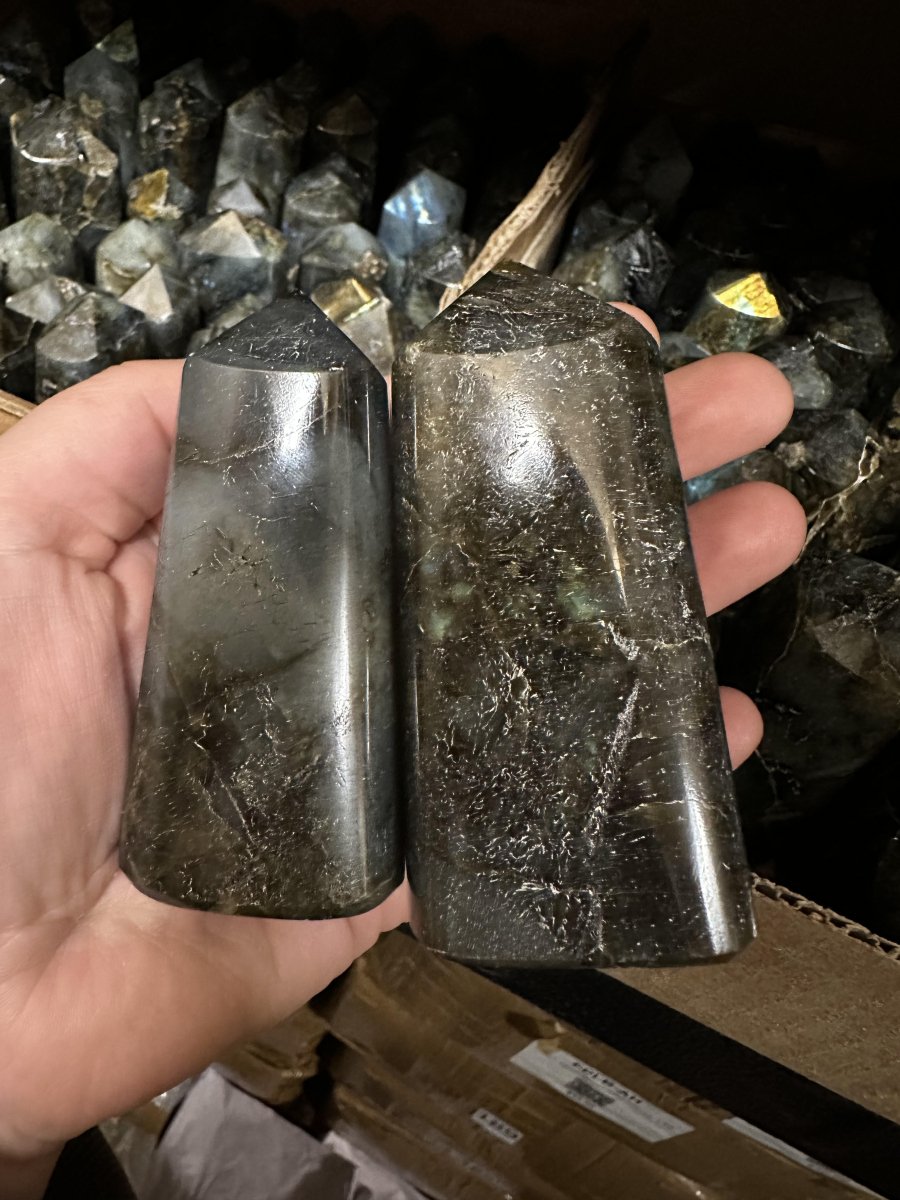
Labradorite
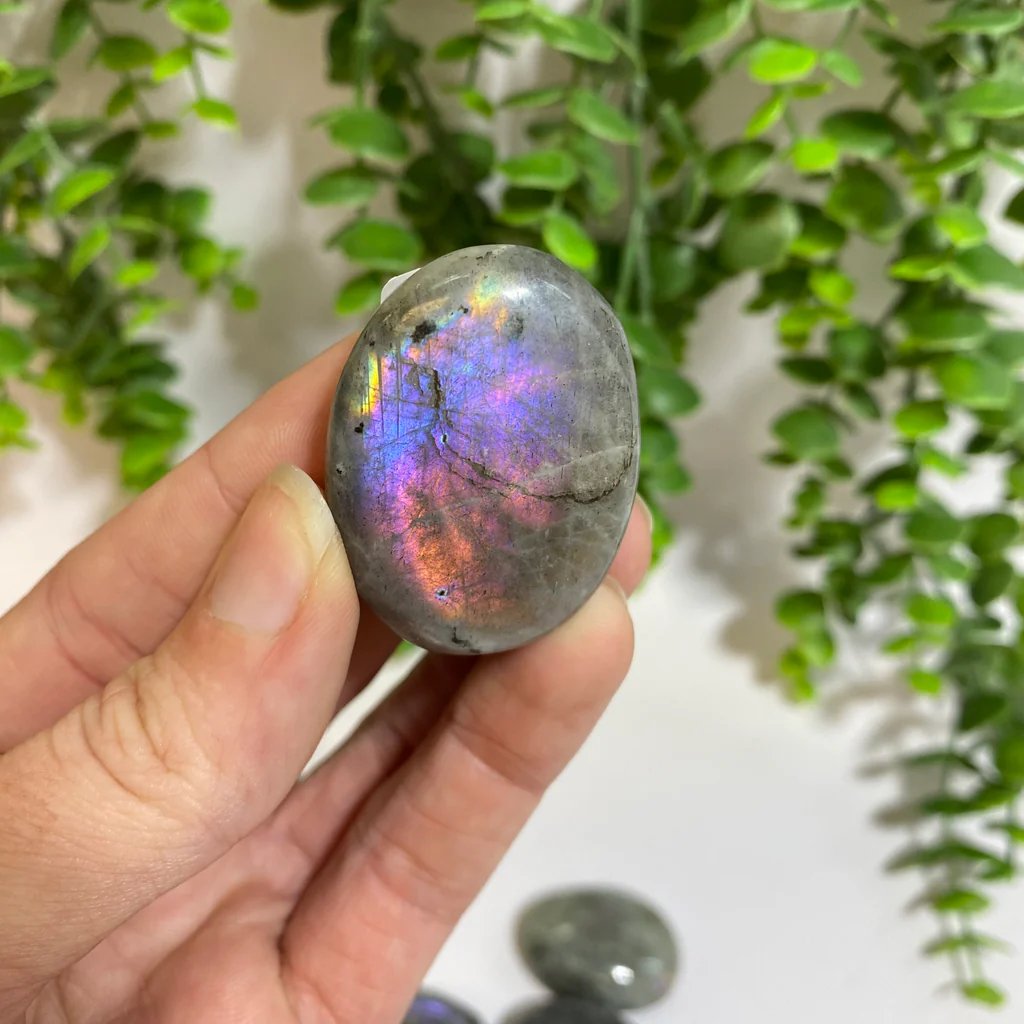
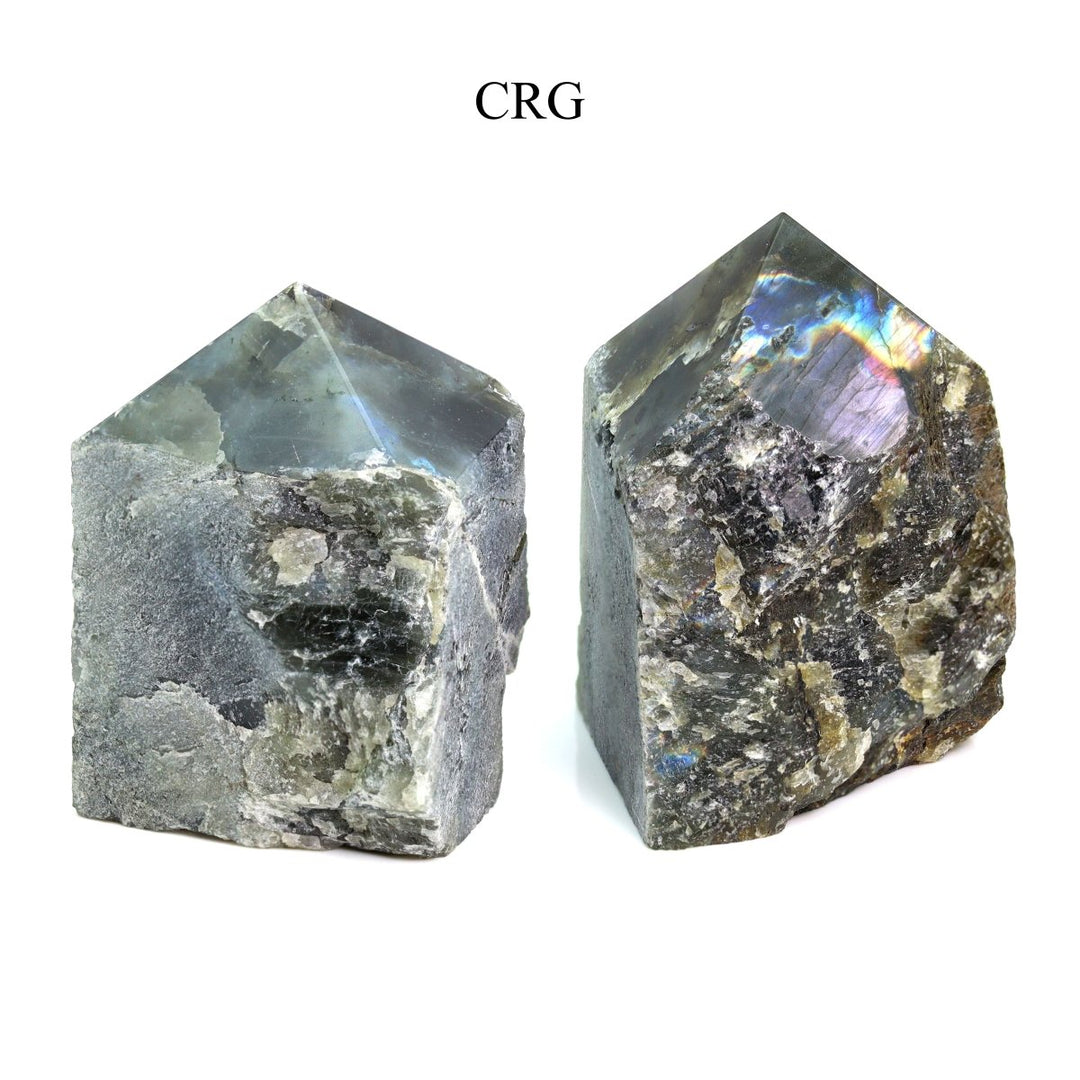
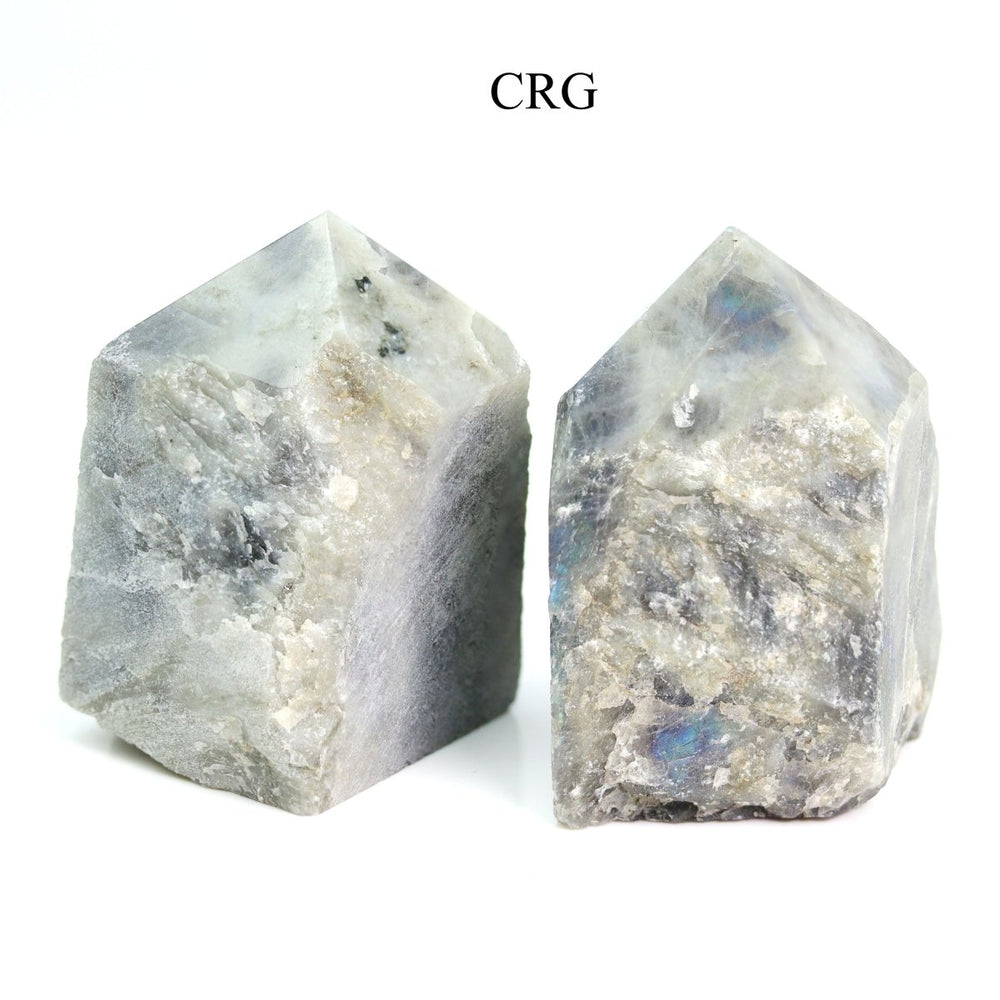
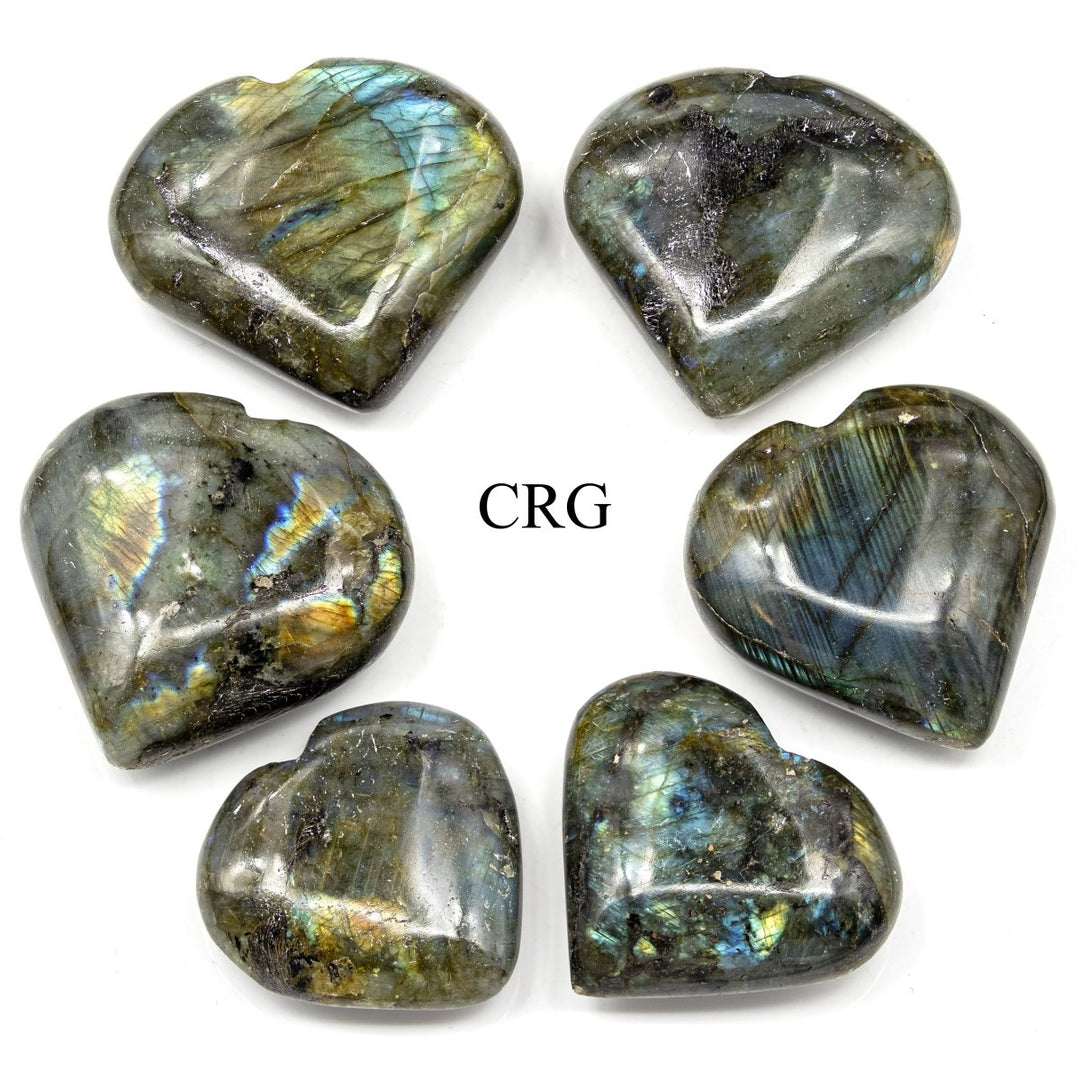
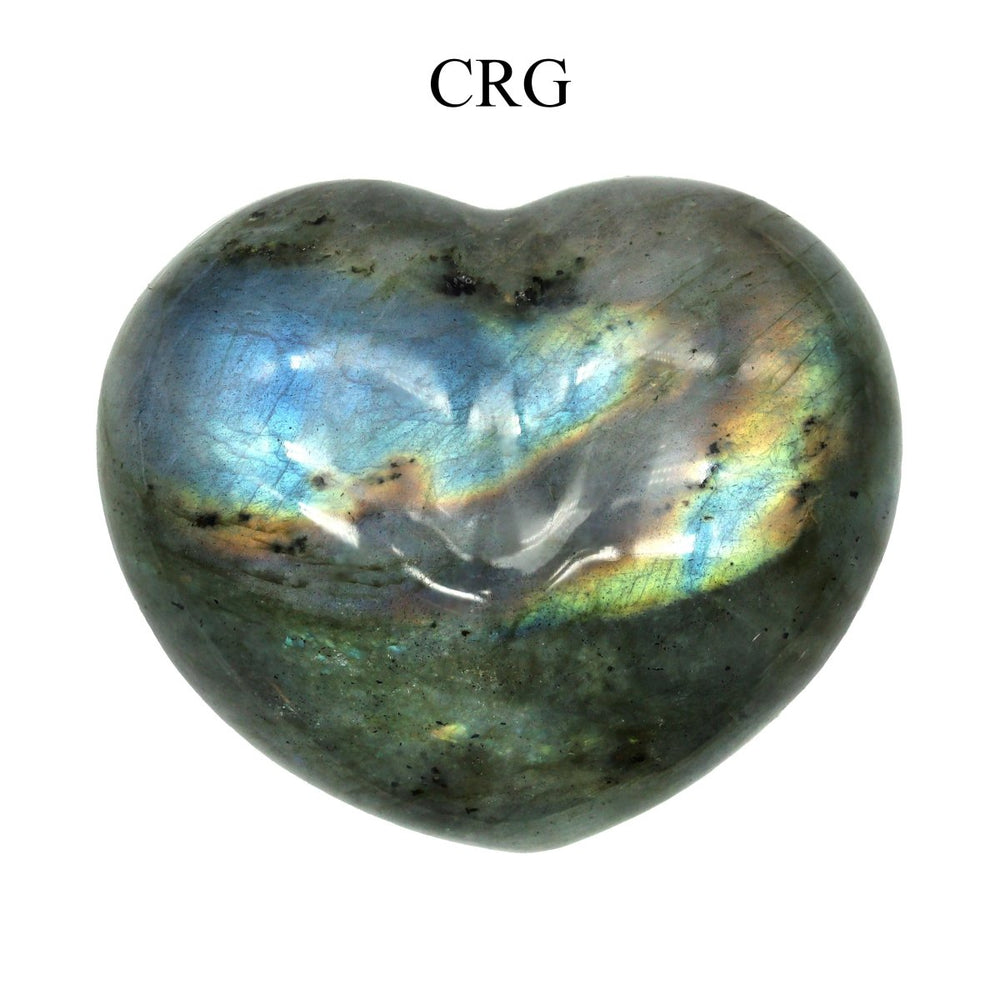
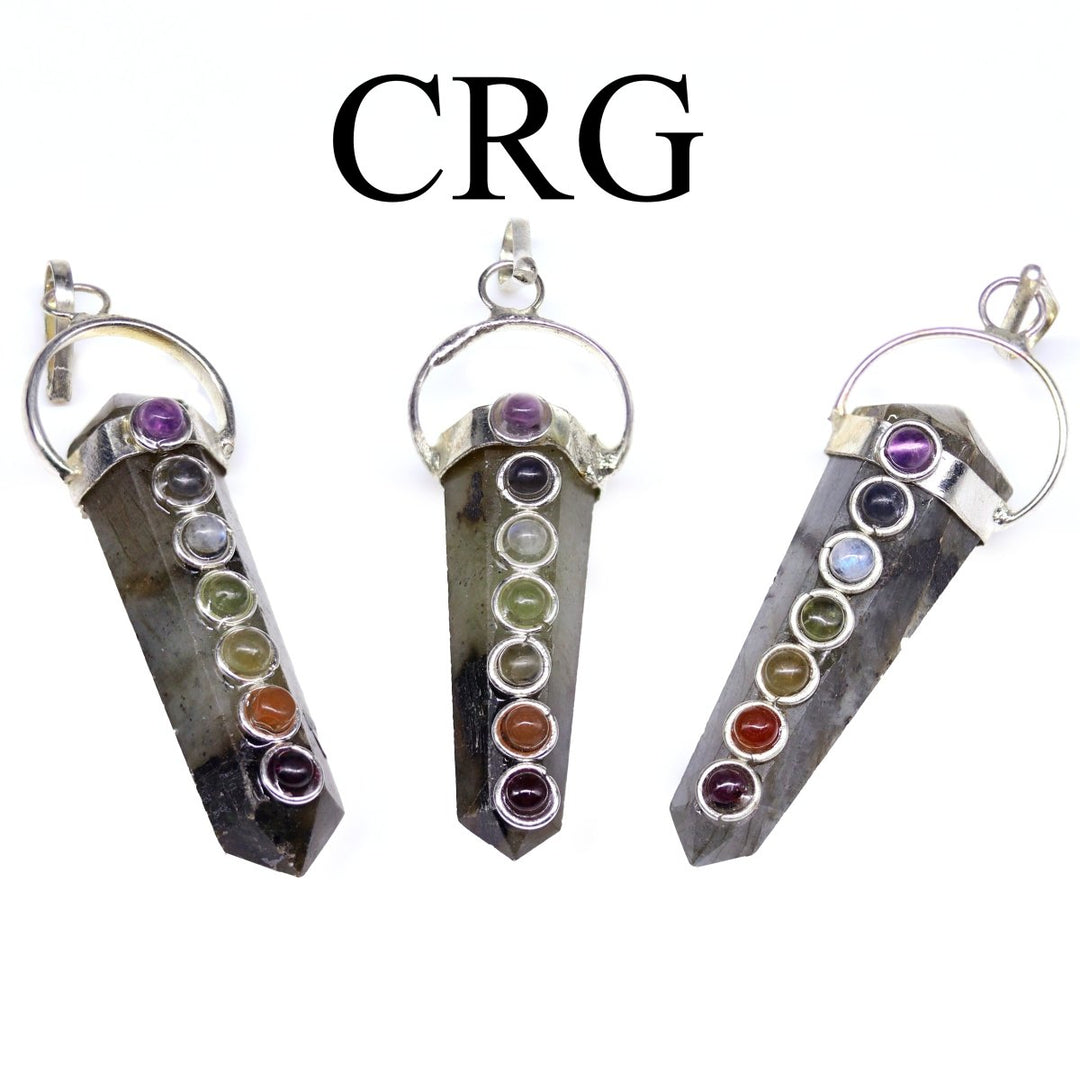
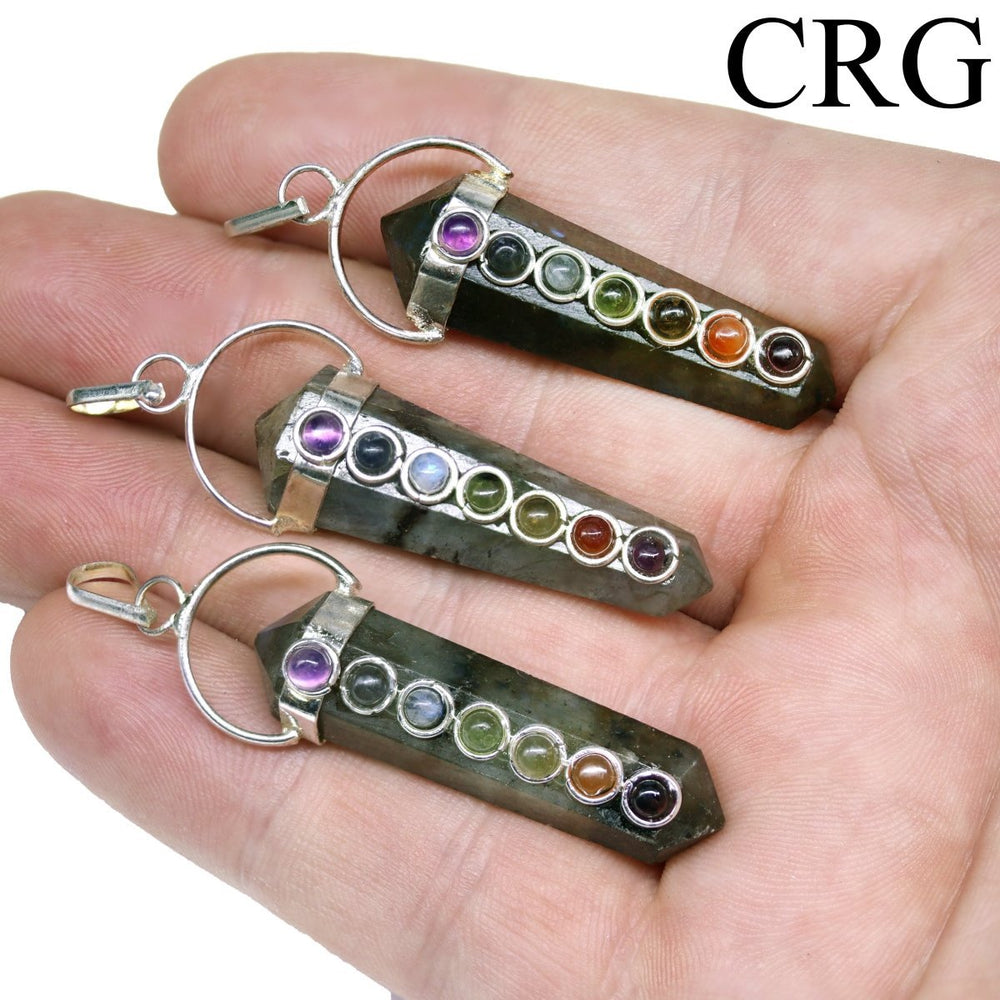
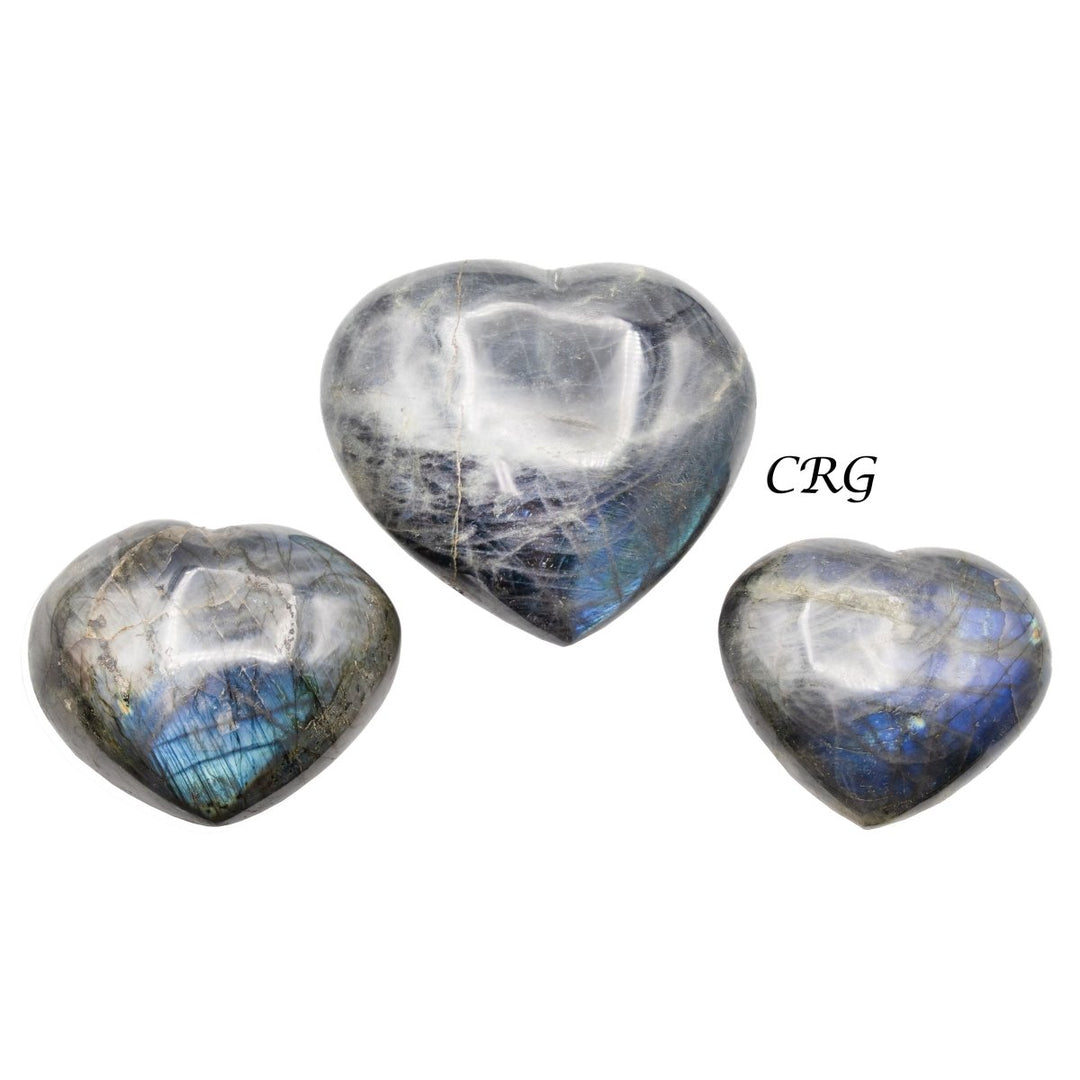
Labradorite is a member of the plagioclase feldspar group and is chemically composed of calcium and sodium aluminum silicate, with the formula (Ca,Na)(Al,Si)_4O_8. It typically forms in mafic igneous rocks such as basalt and gabbro, as well as in anorthosites. It crystallizes from magma as it cools, forming large, well-developed crystals. Labradorite has a hardness of 6 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale, making it relatively durable. Its most distinctive feature is its labradorescence, which results from light diffraction within the lamellar intergrowths inside the crystal. These intergrowths create vibrant blue, green, gold, orange, red, and sometimes purple flashes when the stone is viewed from different angles. Significant deposits of labradorite can be found in Canada, notably in Labrador, after which it is named, as well as in Australia, Madagascar, Mexico, Norway, Russia, and the United States.